Salt belt conveyor
What is Salt belt conveyor?
A salt belt conveyor is a continuous belt conveyor used to transport salt. Common belt materials include corrosion-resistant PVC, PU, and special rubber conveyor belts. The design and selection of these conveyors are determined by specific operating requirements, such as hourly material throughput and conveying distance. Small conveyors can handle tens of tons of material per hour, while larger equipment can handle hundreds or even thousands of tons. They can accommodate conveying distances ranging from tens of meters to thousands of meters.

What are the types of salt belt conveyors?
Salt belt conveyors are used to transport salt. The corrosive nature of salt places special demands on the material of conveyor components, particularly the conveyor belt. Therefore, salt belt conveyors are typically categorized by the belt material to accommodate the chemical properties of salt.
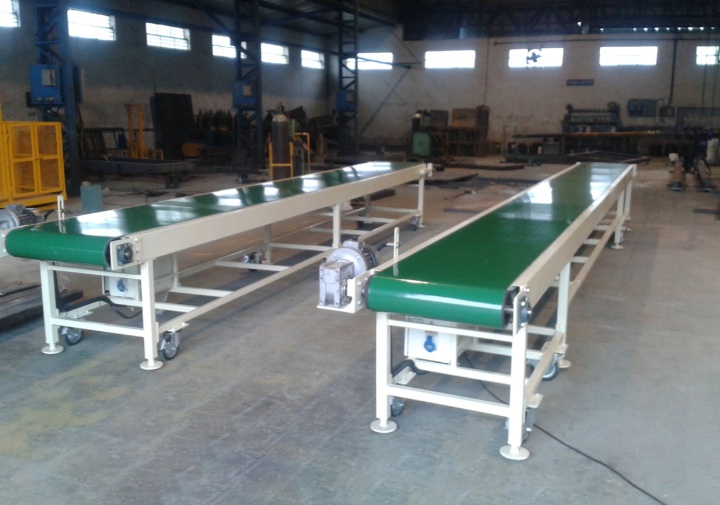
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Conveyor Belt
Features: PVC is relatively inexpensive and offers a certain degree of wear and corrosion resistance.
Applications: Commonly used for conveying common salts such as sea salt and table salt. PVC conveyor belts are an economical and practical choice for applications where belt strength and corrosion resistance are less critical.
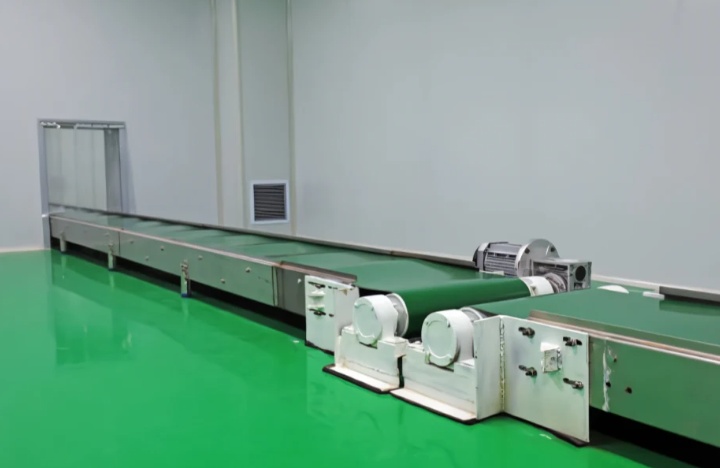

PU (Polyurethane) Conveyor Belts
Features: PU conveyor belts are more wear-resistant than PVC, and are also more resistant to oil and chemical corrosion. They are also soft and meet food hygiene standards.
Applications: They are particularly suitable for conveying food-grade salt, such as refined table salt and seasoning salt. Their superior performance ensures the purity of the salt is not contaminated during transportation.
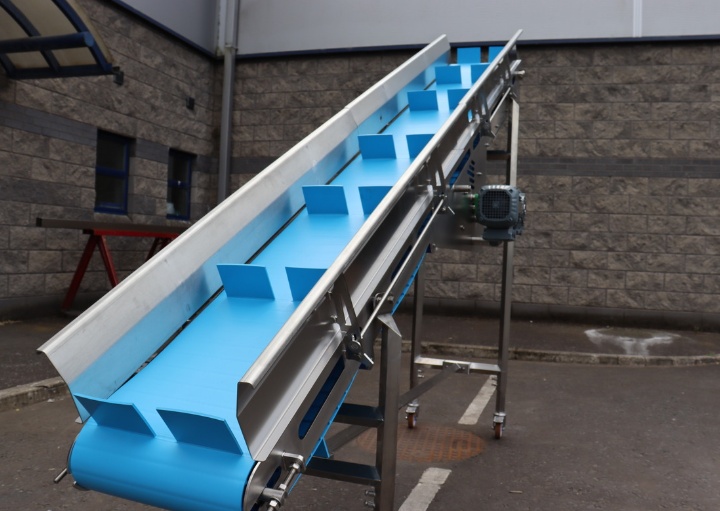

Rubber Conveyor Belts
Features: Rubber conveyor belts offer excellent elasticity and wear resistance, making them adaptable to a variety of complex conveying environments. To enhance corrosion resistance, special acid- and alkali-resistant rubber materials are often used.
Applications: Primarily used for large-scale, long-distance conveyance of industrial salt, such as in mines and docks.
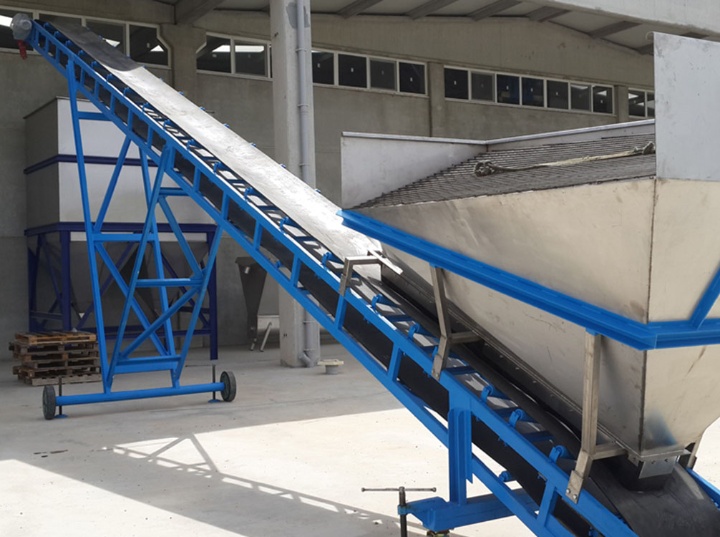

Steel Cord Conveyor Belts
Features: These conveyor belts have an internal steel cord structure, significantly increasing their tensile strength and load-bearing capacity. To prevent corrosion, the steel cord is often covered with a special rubber or polymer coating. Applications: Used in applications with large conveying volumes, long distances, and steep gradients, such as large salt mines and chemical plants. It can withstand extremely high tension, ensuring stable and safe conveying.
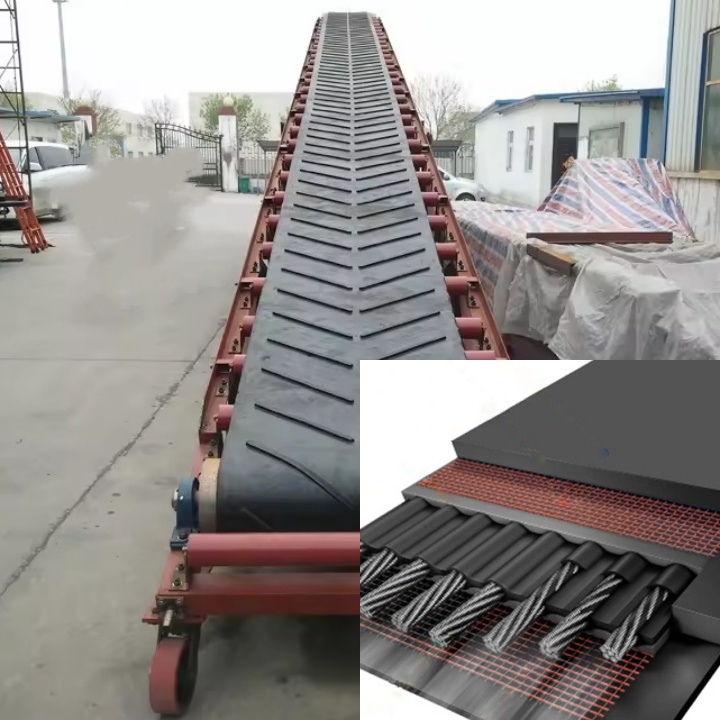

What are the advantages of a salt belt conveyor?
Thanks to its targeted design, the salt belt conveyor offers numerous advantages when handling salt, such as corrosion resistance, sealing, and strong adaptability. This makes it an ideal choice for salt production, processing, and transportation.
Excellent corrosion resistance: Salt, especially industrial salt and sea salt, is corrosive. Ordinary conveying equipment is susceptible to rust and damage after prolonged contact with salt. Salt belt conveyors utilize corrosion-resistant materials, such as treated steel or stainless steel for the frame, and special acid- and alkali-resistant rubber, PVC, or PU conveyor belts. This material combination effectively resists salt corrosion and significantly extends the equipment's service life.
Excellent sealing: Improper handling of salt during conveyance can easily generate dust or leaks, causing material loss and potentially polluting the environment. Salt belt conveyors are typically designed with effective sealing features, such as baffles or skirts at the edges of the conveyor belt, to effectively prevent material spillage. This helps maintain a clean working environment and ensures material integrity.
Adaptability: Salt belt conveyors are adaptable to diverse conveying needs. They can easily handle long distances, large loads, and conveying at varying slopes. Whether transporting from mines to processing plants or loading and unloading at ports, they provide stable, continuous conveying. Furthermore, by adjusting the conveyor belt type, they can also meet the conveying requirements of different salt materials (such as industrial salt, edible salt, and refined salt).
Reduced Maintenance Costs: Compared to other complex conveying systems that require frequent lubrication and part replacement, salt belt conveyors have a relatively simple structure and require less routine maintenance. Due to their superior corrosion and wear resistance, the wear rate of major components is low, reducing the frequency of part replacement and associated maintenance costs. This ensures long-term, stable operation of the equipment.
Salt Belt Conveyor Parameters
|
Belt width (mm) |
Conveying length(m) Power(kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying amount (t/h) |
||
| B400 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 5-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 30-60 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 4-7.5 | |||
| B500 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 40-80 |
| 3 | 4-5.5 | 5.5-7.5 | |||
| B650 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 80-120 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-11 | |||
| B800 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 120-200 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-15 | |||
| B1000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 200-320 |
| 5.5 | 7.5-11 | 11-22 | |||
| B1200 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 290-480 |
| 7.5 | 7.5-15 | 15-30 | |||
| B1400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 400-680 |
| 11 | 15-22 | 22-45 | |||
| B1600 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.25-2.0 | 600-1080 |
| 15 | 22-30 | 30-75 | |||
| B1800 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.0-2.0 | 200-1500 |
| 18.5 | 30-45 | 45-110 | |||
| B2000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1000-2000 |
| 22 | 45-55 | 55-132 | |||
| B2400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1500-3000 |
| 30 | 55-75 | 75-185 | |||
What are the structural features of a salt belt conveyor?
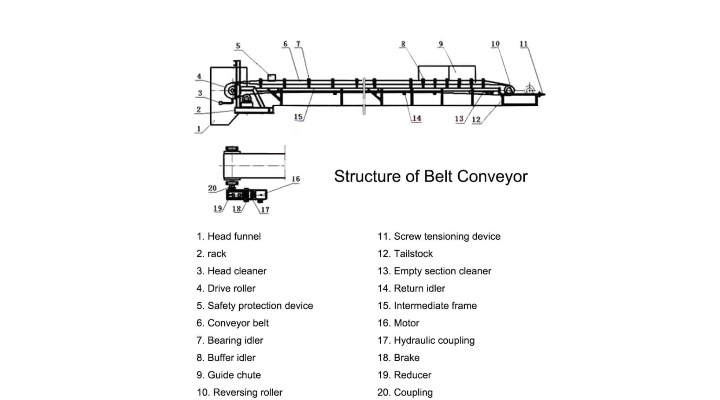
A salt belt conveyor is a continuous conveying device used to transport salt. Its structure primarily consists of a corrosion-resistant conveyor belt, a drive unit that provides power, idlers and tensioning devices that support the belt's smooth operation, and a corrosion-resistant frame that serves as its backbone.
The conveyor belt is the conveyor's primary load-bearing component and comes into direct contact with the salt material. To resist the corrosive effects of salt, it is typically made of specialized acid- and alkali-resistant materials, such as PVC (economical and suitable for general salt transport), PU (more wear-resistant, commonly used for food-grade salt transport), and special rubber (excellent elasticity and wear resistance, suitable for large-volume, long-distance transport).
The drive unit is the conveyor's power source, responsible for driving the conveyor belt. It typically consists of an electric motor, providing the required power. A reducer reduces the motor's speed to a suitable speed for the conveyor belt. A coupling connects the motor and reducer, transmitting torque. The drive roller, also called the drive roller, drives the conveyor belt through friction with the belt.
Idlers: Idlers support the conveyor belt and the material on it, ensuring smooth operation. Based on their function, rollers can be divided into load rollers (located above the conveyor belt, supporting the weight of the material and conveyor belt), return rollers (located below the conveyor belt, supporting the empty conveyor belt on the return journey), and self-aligning rollers (used to correct conveyor belt deviation and prevent belt edge wear).
Frame: The frame is the skeleton of the conveyor, supporting all components. Because it is also exposed to salt corrosion, it is typically made of corrosion-resistant materials. Stainless steel, for example, offers excellent corrosion resistance, but is more expensive. Carbon steel that has undergone special anti-corrosion treatments, such as galvanizing or spraying with anti-corrosion paint, offers improved corrosion resistance and is a more cost-effective option.
Tensioner: The tensioner adjusts the tension of the conveyor belt to prevent it from slipping or deviating during operation. Common tensioning methods include spiral tensioning, which adjusts the tension by adjusting a bolt, and weight tensioning, which automatically maintains tension using the weight of a weight.
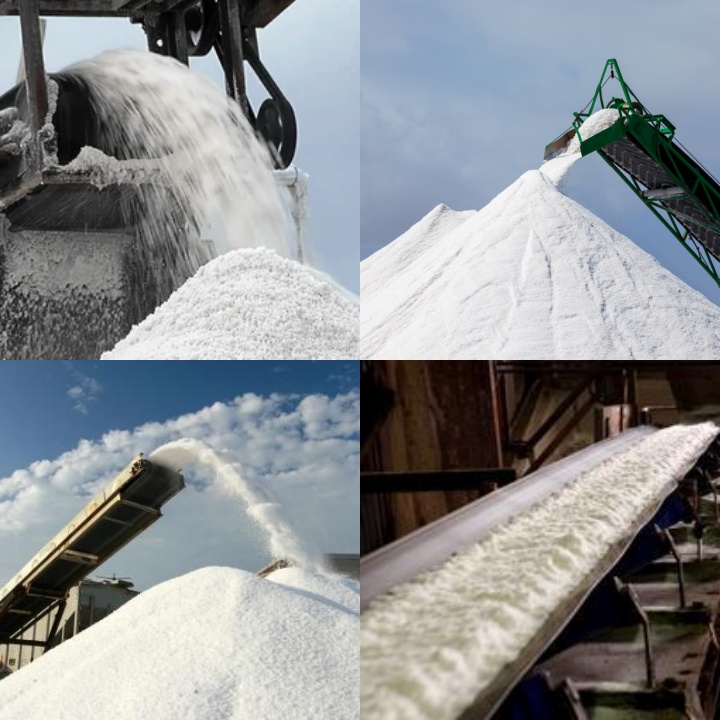
What are the applications of salt belt conveyors?
Salt belt conveyors, due to their corrosion resistance, simple structure, and stable operation, are widely used in various industries that handle salt. Their primary application areas include:
Salt production and processing: This is the core application area for salt belt conveyors. In production lines for various salt types, such as sea salt, lake salt, and well salt, they transport raw salt mined from salt pans, salt lakes, or mines to initial processing or storage. In refined salt plants, they transport refined salt after washing, drying, and crushing to packaging plants or finished product warehouses. In food-grade salt production lines, salt belt conveyors ensure hygienic transport and prevent contamination.
In the chemical industry: Many chemical products use salt or produce salt-containing byproducts during production. Salt belt conveyors are used in these applications for raw material transportation, transporting industrial salt to reactors or mixing equipment. Byproduct conveying: Certain chemical production processes, such as the alkali and chlor-alkali industries, generate large quantities of salt as byproducts. Salt belt conveyors are used to transport and process these byproducts.
Ports and docks: At ports and docks, large quantities of salt products require loading, unloading, transshipment, and storage. Salt belt conveyors play a vital role in this process. Ship loading and unloading: They are used to unload bulk salt from ships or load salt onto ships. Material transfer: Within docks, they are used to transport salt from one area to another for short-distance transportation or distribution.

Salt belt conveyors have demonstrated their reliability in handling salt materials in practical applications. Their corrosion-resistant conveyor belts and frames resist the effects of salt on components, ensuring long-term operation. They enable continuous material transfer in a variety of application scenarios and can be integrated with other equipment to form a complete material handling system. Their relatively simple structure facilitates routine inspection and maintenance. This conveyor provides a continuous handling method for salt materials, ensuring stable production and logistics links.
