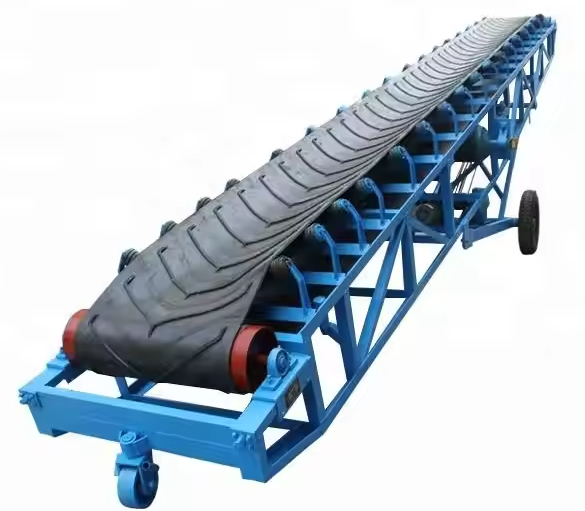
Coal belt conveyor
What is Coal belt conveyor?
Coal belt conveyors are widely used equipment. Their core function is to achieve continuous, directional transport of coal. They come in a variety of designs and structures, including general-purpose fixed and retractable types, as well as steel cord and solid braided belts, to suit varying operating conditions. They typically handle hundreds to thousands of tons of material per hour, and single-line conveying distances can range from tens of meters to several kilometers or even longer.

What are the types of coal belt conveyors?
Coal belt conveyors can be categorized into various types based on different classification criteria. There are two main types of conveyor belts, based on the belt core material. Steel cord conveyor belts are suitable for long-distance, high-capacity, and high-strength conveying; solid braided conveyor belts are designed for medium- and short-distance conveying with special requirements for tear and impact resistance.
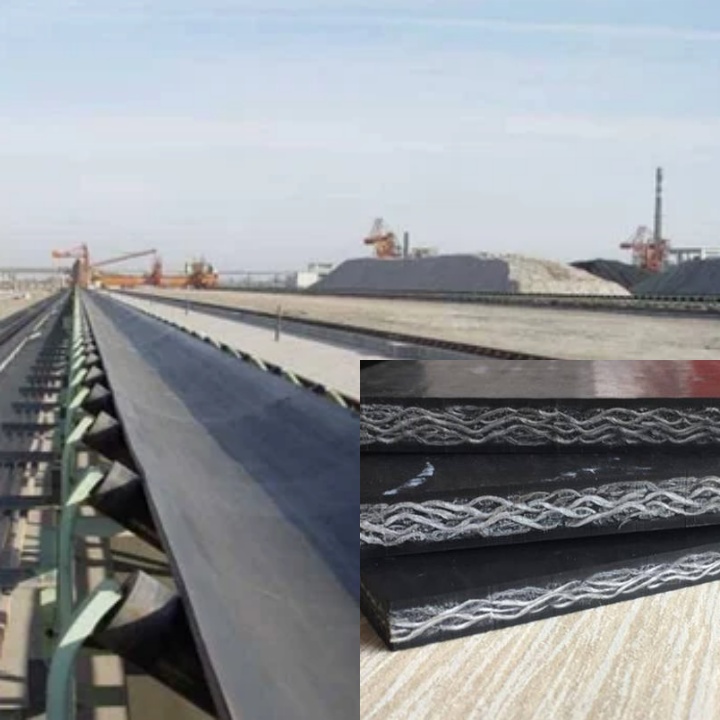
Steel Cord Conveyor Belts
The core of these conveyor belts is composed of multiple high-strength steel cords arranged in parallel and encased in a rubber material. This structure gives steel cord conveyor belts high tensile strength and impact resistance. Key Features: High strength and the ability to withstand significant tensile forces make it particularly suitable for long-distance, high-volume coal transportation, effectively reducing the number of conveyors and transfer stations. Low elongation: Because the belt core is made of steel wire rope, its elastic elongation is minimal, ensuring stable operation and preventing deviation. Excellent impact resistance: Capable of withstanding significant impact, especially at drop points, effectively protecting the belt from damage. Widely applicable, it is widely used in large coal mines, ports, power plants, and other locations with high requirements for conveying capacity and distance.
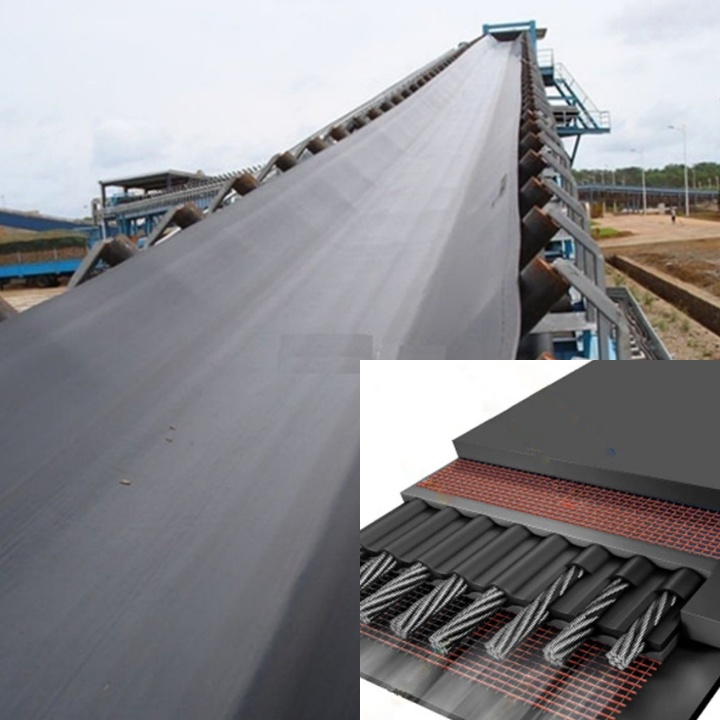

Solid Braided Conveyor Belts
Solid braided conveyor belts feature a core made of high-strength synthetic fibers (such as polyester and nylon) through a specialized braiding process. This core is formed from a single piece without layers.
Key Features: Excellent tear resistance: Due to its solid braid structure, tears are less likely to propagate when penetrated by sharp objects, effectively preventing longitudinal tears. High impact resistance: The braided structure provides excellent energy absorption, effectively resisting the impact of drop shock. Solid braided belts feature high joint strength. The joints are typically hot-vulcanized, resulting in high joint strength that rivals or approaches the strength of the belt itself. Solid braided belts are also lightweight compared to steel cord conveyor belts, making them easier to install and maintain. They are primarily used for medium- to short-distance conveyances requiring high tear and impact resistance, such as underground tunnels or stockpiles.

What are the advantages of coal belt conveyors?
Coal belt conveyors are essential core equipment in industries like coal mines and power plants. Their high efficiency, flexibility, adaptability, and safety make them a key component of material handling systems. The following are their key advantages:
Continuous conveying: Belt conveyors enable continuous, uninterrupted material transportation. They offer high conveying capacities, with a single unit capable of transporting thousands of tons of coal per hour. This continuous operation significantly improves production efficiency, reduces material transfer steps, and thus reduces labor and time costs.
Flexible conveying distance and angle: Belt conveyors are capable of long-distance conveying, particularly in modern coal mines and large coal storage yards, connecting different production areas.
High-angle conveying: By utilizing specialized conveyor belts (such as high-angle corrugated sidewall conveyor belts), belt conveyors can transport materials at steep angles. This offers significant advantages in environments with slopes or limited space, such as underground tunnels, effectively saving floor space and construction costs.
Stable operation: Belt conveyors have a simple structure and a stable and reliable operating principle. Compared to other conveying methods, such as truck transport, they consume less energy. They experience low resistance during operation and consume relatively little drive power, which helps reduce operating costs.
Safety and good sealing: Fully enclosed or tubular belt conveyors effectively prevent dust and material spillage caused by wind or vibration during coal transportation. Belt conveyors are often equipped with various safety features, such as anti-slip, anti-tear, and pull-cord emergency stop devices, to promptly detect and address potential malfunctions, ensuring the safety of both equipment and personnel.
Strong Adaptability: Belt conveyors can be deployed to suit various terrains and environments, operating on the surface, underground, in tunnels, or on trestles. They can adapt to a variety of complex working conditions, and suitable belt conveyor solutions can be found for both open-pit and underground mines.

Coal Belt Conveyor Parameters
|
Belt width (mm) |
Conveying length(m) Power(kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying amount (t/h) |
||
| B400 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 30-60 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 4-7.5 | |||
| B500 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 40-80 |
| 3 | 4-5.5 | 5.5-7.5 | |||
| B650 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 80-120 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-11 | |||
| B800 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 120-200 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-15 | |||
| B1000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 200-320 |
| 5.5 | 7.5-11 | 11-22 | |||
| B1200 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 290-480 |
| 7.5 | 7.5-15 | 15-30 | |||
| B1400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 400-680 |
| 11 | 15-22 | 22-45 | |||
| B1600 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.25-2.0 | 600-1080 |
| 15 | 22-30 | 30-75 | |||
| B1800 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.0-2.0 | 200-1500 |
| 18.5 | 30-45 | 45-110 | |||
| B2000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1000-2000 |
| 22 | 45-55 | 55-132 | |||
| B2400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1500-3000 |
What is the structure of a coal belt conveyor?
A coal belt conveyor is a complex mechanical system designed to transport coal continuously, stably, and reliably. While details vary between conveyor models, its basic structure generally consists of the following main components:
Conveyor Belt: The conveyor belt is the core component of the conveyor, directly carrying and moving the material. Depending on the material, common examples include ordinary fabric belts made of fibers such as cotton, nylon, or polyester, suitable for short to medium-distance conveying with moderate loads. Steel cord conveyor belts, with a high-strength steel cord core and extremely high tensile strength, are suitable for long-distance, high-capacity, and high-load conveying. Solid braided belts, made of a single-piece woven synthetic fiber, offer excellent tear resistance and are suitable for applications requiring high tear resistance. Drive unit: The drive unit is the part that powers the conveyor belt, ensuring continuous operation. It typically consists of a motor (providing the power source), a speed reducer (reducing the motor's speed while increasing torque to meet the conveyor's drive requirements), and a drive roller (driving the conveyor belt through friction. The drive roller is often coated with rubber to increase friction).
Tensioning device: The tensioning device adjusts the tension of the conveyor belt to prevent it from slipping or deviating during operation. There are two main types of tensioning devices. Weight-type tensioning uses the weight of a weight to apply constant tension, offering a simple and reliable structure. Electric winch-type tensioning uses a motor and winch to adjust tension, offering more precise and flexible control.
Frame: The frame is the skeleton of the conveyor, supporting and securing all components and maintaining their relative position. It is typically constructed of welded or bolted steel.
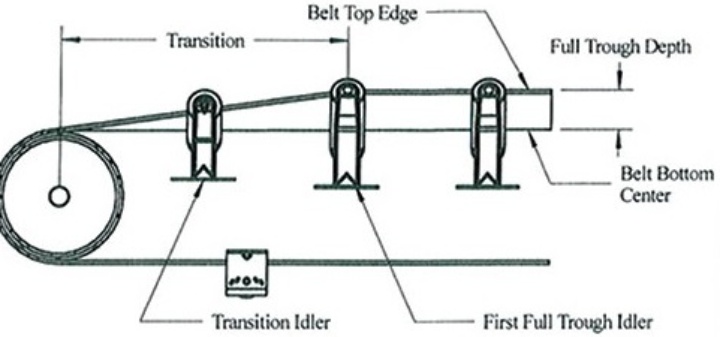
What are the applications of coal belt conveyors?
As a material handling device, the coal belt conveyor is a critical component in many large-scale production and logistics processes. It is primarily used for continuous, large-volume, and long-distance conveyance of bulk materials. The following are some of the most common applications of coal belt conveyors, not specifically industry specific:
Mining and Extraction: In various mining operations, belt conveyors are the lifeline connecting the extraction site to surface processing facilities. Whether in open-pit or underground mines, they transport mined raw coal from the working face to surface stockpiles, coal preparation plants, or loading stations. This continuous conveying method improves mining efficiency and reduces the cost and environmental impact of vehicle transportation.
Energy and Power Generation: In thermal power plants, belt conveyors are the core of the coal supply system. They continuously transport coal from the unloading dock, train platform, or coal storage yard to the pulverizer or boiler fuel bunker. This automated conveying process ensures a stable and continuous fuel supply to the power plant and is an essential infrastructure for power generation.
Ports and Terminal Logistics: In ports, belt conveyors are used to load and unload large bulk carriers. They efficiently unload coal from ship holds to dock yards, or load coal from the yard onto ships. This significantly reduces ship berthing time, improving port throughput and operational efficiency. Chemical and Metallurgical Industries: In these industries, belt conveyors are widely used not only to transport coal but also to transport raw materials such as coke, ore, and limestone. In steel mills, they transport coke, iron ore, and other materials to blast furnaces; in chemical plants, they transport various powdered or granular raw materials to ensure continuous production line operation.
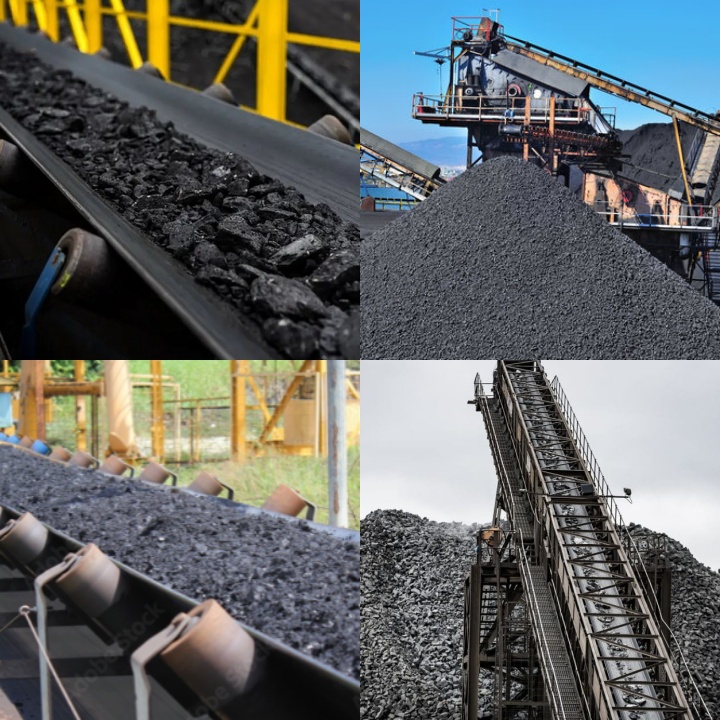

As a fundamental material handling equipment, the coal belt conveyor's function lies in the stable transfer of coal. Its continuous operation mode ensures uninterrupted material flow. Its adaptability to various terrains allows it to be deployed in horizontal, inclined, and even complex spaces, reducing site constraints. These characteristics form the foundation for the coal belt conveyor's application in industrial material handling. In practice, this equipment is typically configured to meet specific conveying requirements based on specific site conditions and material characteristics.

