Rubber belt conveyor
What is Rubber belt conveyor?
Rubber belt conveyors are essential material handling equipment. These types can be categorized into various types based on their structure and function, including fixed, mobile, telescopic, and high-angle conveyors with sidewalls. In practice, belt conveyors can handle a wide range of material volumes, from tens to thousands of tons per hour. They also offer great flexibility in conveying distances, ranging from a few meters to tens of kilometers, providing a variety of solutions for production and logistics needs of varying scales.
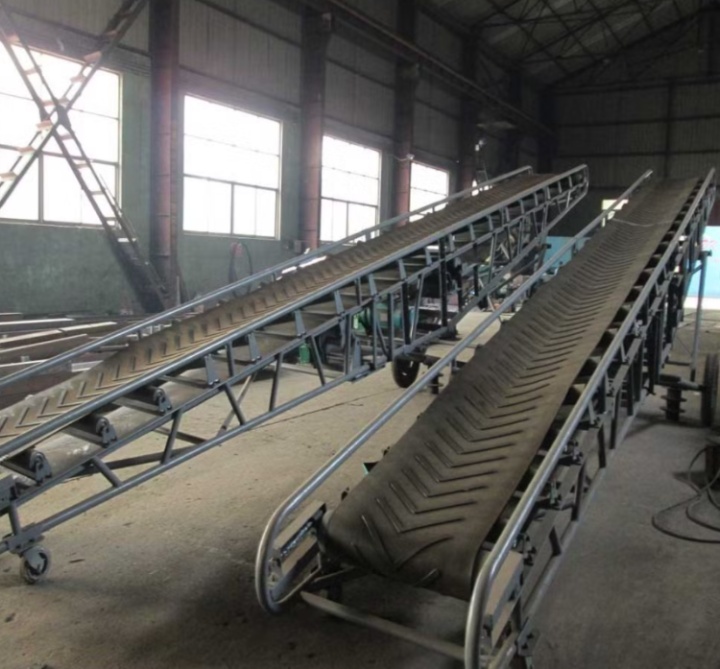

What are the types of rubber belt conveyors?
Rubber belt conveyors can be categorized into various types based on their structure and function. Common types include mobile, telescopic, and high-angle belt conveyors. The following is a detailed introduction to these common types:
Mobile Belt Conveyor
Mobile belt conveyors are characterized by their mobility. They typically consist of a wheeled base and an adjustable-height conveyor body. This design allows for easy transfer between different work sites, making them highly flexible.
Working Principle: A motor drives rollers, which continuously rotate the conveyor belt, transporting materials from one location to another. Because the base is equipped with wheels, it can be pushed manually or towed by a vehicle, enabling quick changes in material loading and unloading locations.
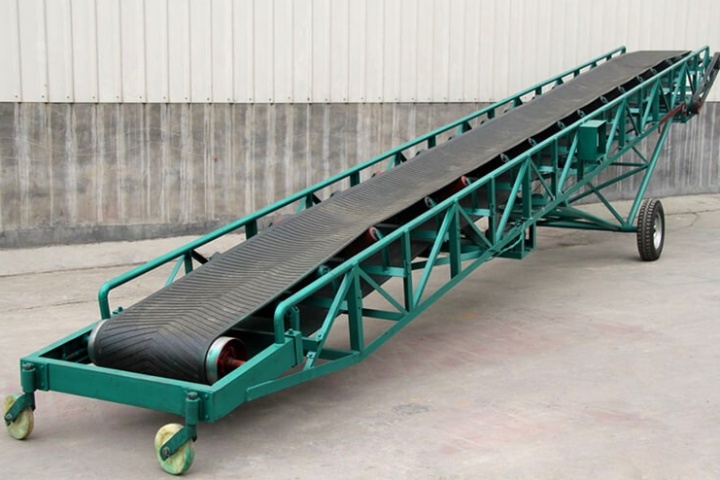

Telescopic Belt Conveyor
The core function of a telescopic belt conveyor is its telescopic nature. Its body can be freely extended or retracted like a telescope to accommodate varying conveying distances.
Operating Principle: It consists of multiple sections of a telescopic body, which are controlled by a control system to adjust the effective length of the conveyor belt. When materials need to be transported to a longer distance, the body is extended; when the conveying distance is shorter, the body is retracted.

High-Angle Belt Conveyor
The outstanding advantage of a high-angle belt conveyor is that it can convey materials at a steep angle, even achieving near-vertical lift. This is extremely useful in applications where ordinary belt conveyors are unable to cope.
Operating Principle: To prevent materials from rolling off at steep angles, this type of conveyor belt typically employs a special structure, such as corrugated sidewalls or partitions installed on the conveyor belt to form "hoppers." These "hoppers" hold the material within, allowing it to be lifted along the conveyor belt at a steep angle.
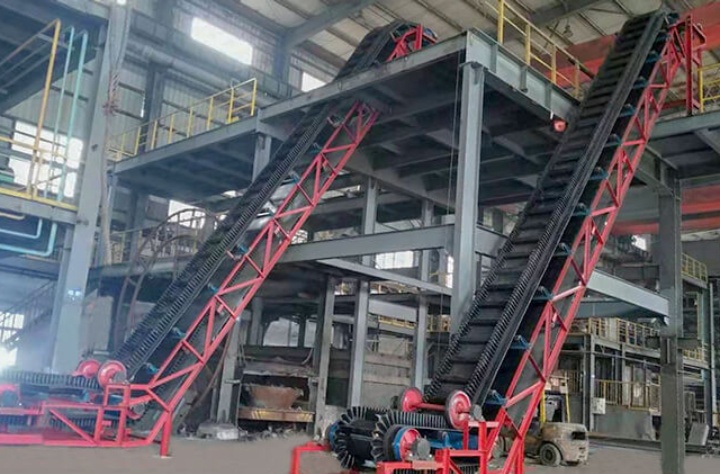

What are the advantages of rubber belt conveyors?
Rubber belt conveyors can stably transport a variety of materials, boasting high capacity and long distances, adapting to a variety of complex working conditions. Due to their simple structure and smooth operation, they are very easy to maintain. The following is a detailed introduction to their key advantages:
High Conveying Capacity and High Efficiency: Rubber belt conveyors can continuously and stably convey a variety of materials. Their high conveying capacity allows them to adapt to the needs of various working environments. They can handle both bulk materials (such as coal, ore, and sand and gravel) and piece items (such as packages and boxes).
Long Conveying Distances and Wide Applications: Rubber belt conveyors can transport materials over long distances, from a few meters to tens of kilometers. They can be flexibly configured to meet specific needs, enabling horizontal, inclined, and even steeply angled conveying, effectively adapting to complex terrain and process requirements.
Smooth Operation and Low Noise: Due to the low friction between the conveyor belt and rollers, coupled with minimal vibration during operation, rubber belt conveyors operate smoothly and quietly. This not only provides a quieter working environment but also helps reduce impact and damage to materials.
Simple structure and easy maintenance: The conveyor's structure is relatively simple, primarily consisting of a conveyor belt, drive unit, rollers, and frame. This makes installation and maintenance relatively easy, and routine inspection and component replacement are minimal.

Rubber belt conveyor parameters
|
Belt width (mm) |
Conveying length(m) Power(kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying amount (t/h) |
||
| B400 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 5-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 30-60 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 4-7.5 | |||
| B500 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 40-80 |
| 3 | 4-5.5 | 5.5-7.5 | |||
| B650 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 80-120 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-11 | |||
| B800 | ≤10 | 12-15 | 15-30 | 1.25-2.0 | 120-200 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 7.5-15 | |||
| B1000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 200-320 |
| 5.5 | 7.5-11 | 11-22 | |||
| B1200 | ≤10 | 10-20 | 20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 290-480 |
| 7.5 | 7.5-15 | 15-30 | |||
| B1400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.25-2.0 | 400-680 |
| 11 | 15-22 | 22-45 | |||
| B1600 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.25-2.0 | 600-1080 |
| 15 | 22-30 | 30-75 | |||
| B1800 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-50 | 1.0-2.0 | 200-1500 |
| 18.5 | 30-45 | 45-110 | |||
| B2000 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1000-2000 |
| 22 | 45-55 | 55-132 | |||
| B2400 | ≤10 | 10-20 | <20-40 | 1.0-2.0 | 1500-3000 |
| 30 | 55-75 | 75-185 | |||
What are the structures of a rubber belt conveyor?
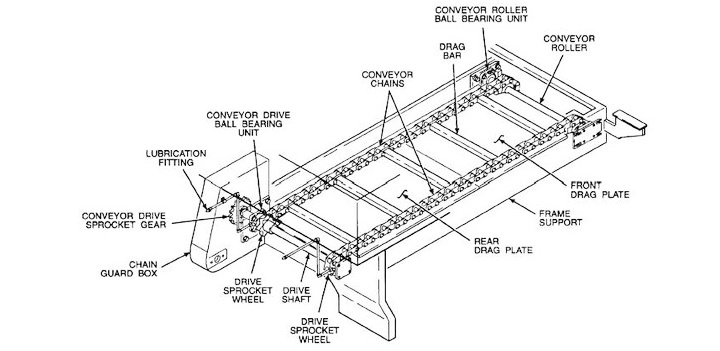
A rubber belt conveyor is a common continuous conveying device with a relatively simple structure yet powerful functionality. A rubber belt conveyor consists of a conveyor belt that carries the material, a drive unit that provides power, rollers and idlers that support and redirect the material, a frame that secures all components, and a tensioning device that maintains tension.
Conveyor belt: The conveyor belt is a critical component of a rubber belt conveyor and serves as the medium for carrying and conveying materials. It typically consists of a core made of multiple layers of canvas (such as polyester, nylon, or cotton canvas) or steel cord, covered with one or more layers of rubber. Conveyor belts vary depending on the nature of the conveyed material, such as heat-resistant, oil-resistant, acid- and alkali-resistant, or flame-retardant.
Drive: The drive provides power to the entire conveyor. It typically consists of a motor, a reducer, a coupling, and a brake. The motor converts high-speed rotation into low-speed, high-torque through the reducer, which is then transmitted to the drive roller via the coupling, thereby driving the conveyor belt.
Rollers: Rollers are crucial support and driving components of the conveyor and are typically divided into drive rollers (transmission rollers), bend rollers (tail rollers), and tensioning rollers.
Idlers: Idlers support the conveyor belt and material and are primarily classified as load-bearing and return rollers.
Frame: The frame is the backbone of the conveyor, securing all components, including rollers, idlers, and the drive. It is typically constructed of welded steel to ensure sufficient strength and stability during operation.
Tensioner: The tensioner maintains proper belt tension, ensuring sufficient friction between the belt and the drive roller to prevent slippage. It also compensates for belt length changes caused by stress or temperature fluctuations. Common tensioning devices include screw, weight, and hydraulic types.
What are the uses of rubber belt conveyors?
The primary purpose of a rubber belt conveyor is to achieve continuous, automated material handling. It plays a key role in numerous scenarios, and its main uses can be summarized as follows:
Conveying bulk materials: Rubber belt conveyors can handle a variety of bulk materials. Whether fine powders, granules, or large pieces, they can be smoothly transported from one point to another via a continuously operating conveyor belt. This significantly reduces manual handling workload and improves material handling efficiency.
Conveying piece items: In addition to bulk materials, belt conveyors are also commonly used to convey piece items. For example, in logistics centers, they can automatically transport packages and boxes; on production lines, they can handle semi-finished or finished parts; and in warehouses, they can help load and unload bagged items.
Connecting different work processes: Belt conveyors often serve as a "bridge" in production processes or logistics systems, seamlessly connecting different work processes. It can transport materials from one processing unit to another, or from the end of a production line to the packaging area, thus forming an automated workflow.
Achieve long-distance or high-height conveying: Thanks to their combinable and configurable nature, belt conveyors can easily transport materials over long distances. Furthermore, by designing inclined conveyors, they can also handle materials across different heights (such as between floors), effectively solving problems in areas with limited space or complex terrain.
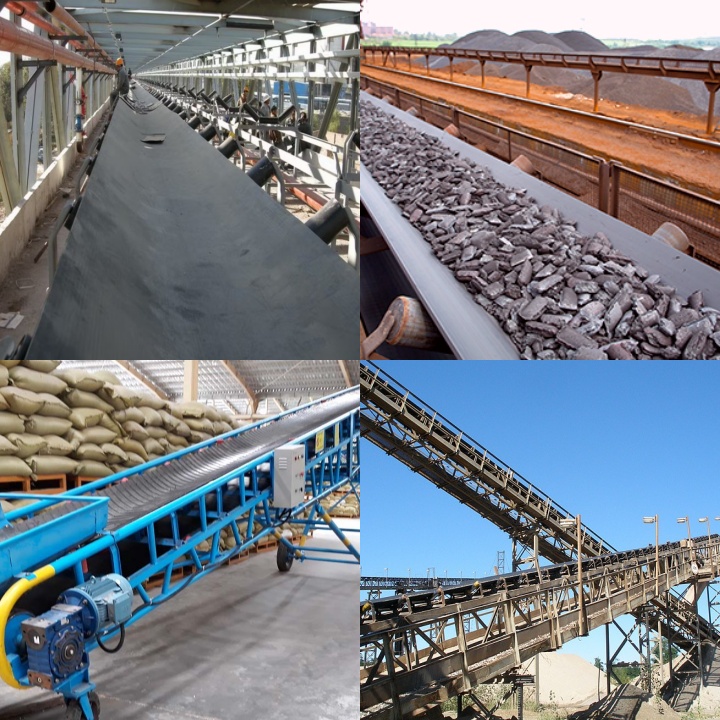

Rubber belt conveyors are widely adopted due to a number of significant advantages. First, their relatively simple structure, consisting primarily of a conveyor belt, drive unit, rollers, and frame, makes installation and maintenance relatively easy. Second, they maintain stable operation, with minimal vibration as materials move along the conveyor belt, minimizing impact on the material itself. These features make rubber belt conveyors a practical and reliable material conveying solution.
