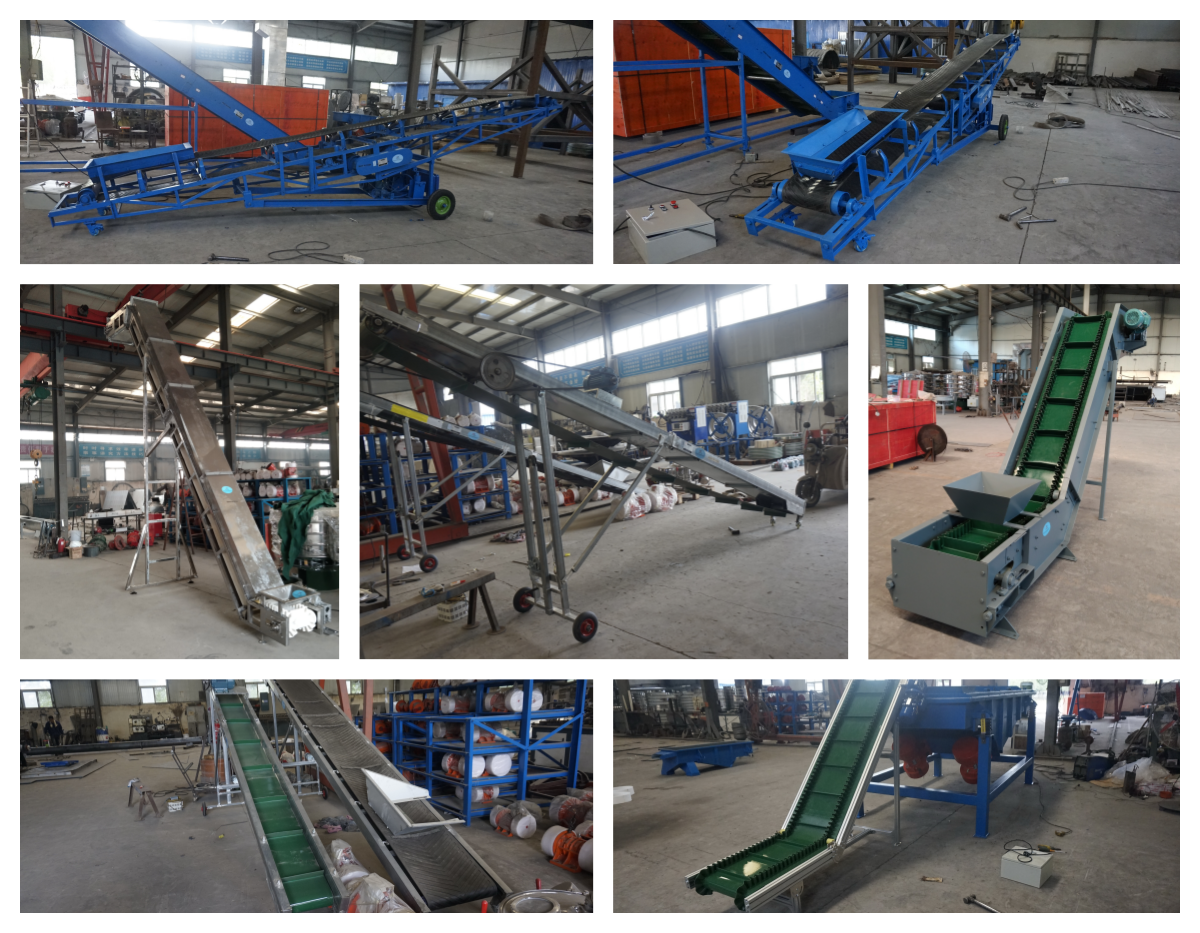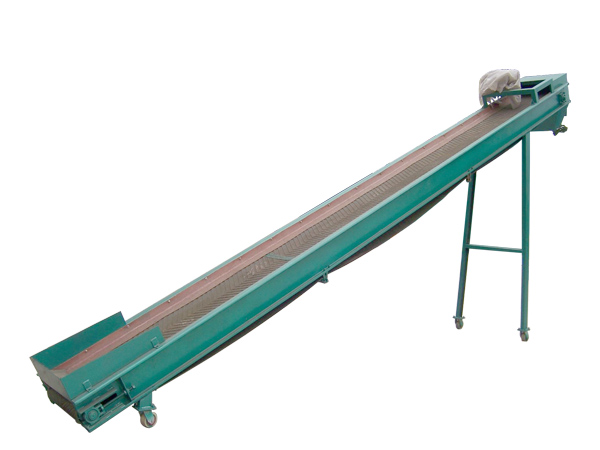
Belt Conveyor Aggregate
Belt conveyor aggregate refers to the process and application of using belt conveyors to transport granular building materials such as sand, gravel, and crushed stone. It can efficiently transport aggregates from one location to another, such as from a quarry to a crushing and screening equipment, or from an aggregate yard to a concrete mixing plant.
Bandwidth: Common bandwidths are 500mm, 650mm, 800mm, 1000mm, etc.
Belt speed: Common belt speeds for aggregate transportation are 1.0~2.5 m/s
Groove angle: Usually 20°~35°
Filling factor: Aggregates are generally 0.6~0.8
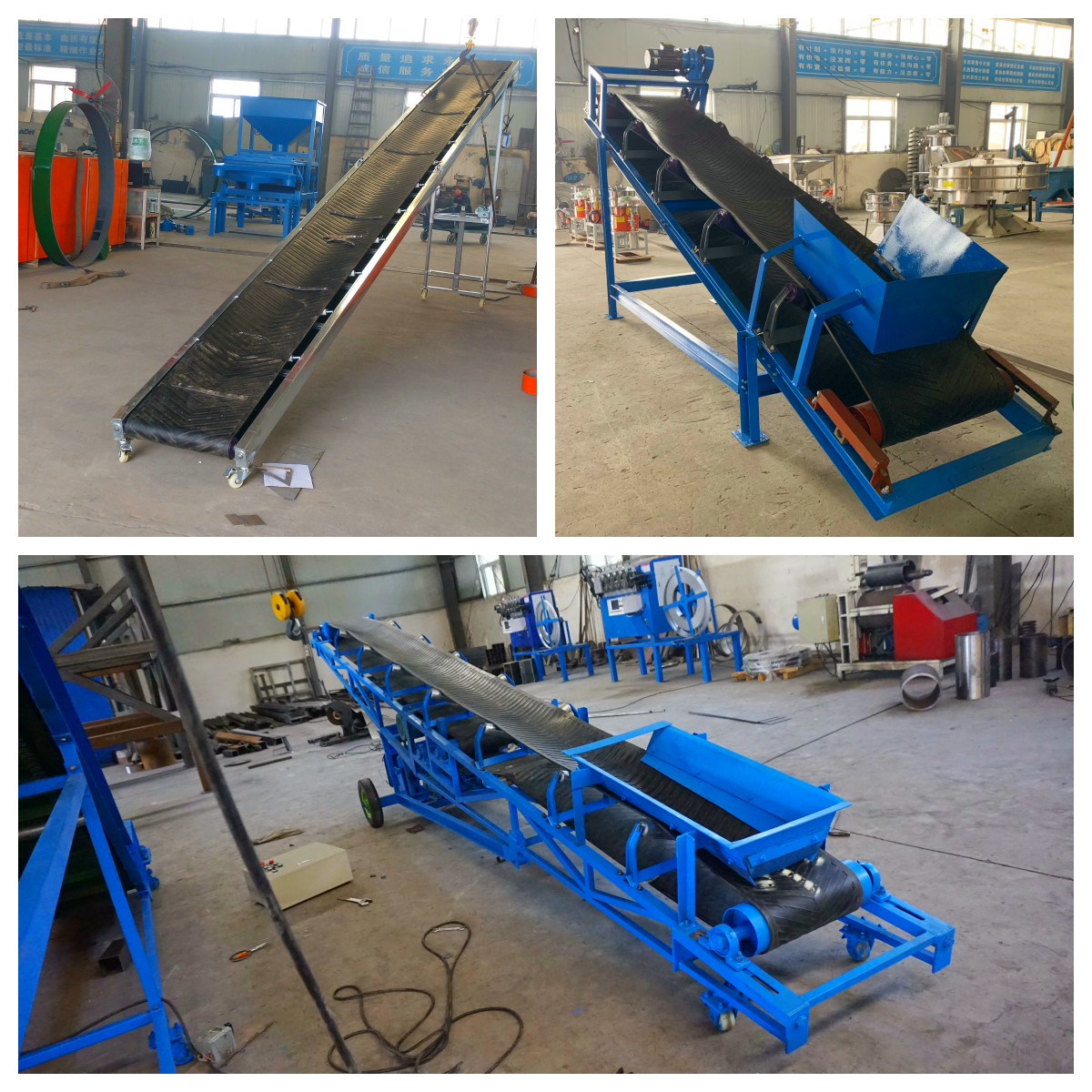

Belt conveyors aggregate usually refer to the working conditions and equipment configuration of using belt conveyors to transport aggregate materials. In industries such as construction projects, concrete mixing plants, quarries, and sand and gravel plants, aggregates (such as crushed stone, sand, gravel, etc.) are common bulk materials, and belt conveyors are important equipment for efficient and continuous transportation of these materials.
Material characteristics of aggregate transportation
Aggregates have the following basic characteristics:

Various particle sizes: from fine sand less than 5mm to crushed stones of tens of millimeters or even hundreds of millimeters.
High density: The bulk density of common crushed stone aggregates is 1.5~1.8t/m³.
Strong wear resistance: Hard crushed stone has greater wear on conveying equipment, especially belt surfaces, rollers and other components.
More dust: Especially in dry production lines, dust is easy to overflow during transportation.
Common forms of belt conveyors aggregate
In aggregate conveying systems, belt conveyors aggregate are one of the core equipment. According to their structural characteristics and usage methods, common forms mainly include: fixed belt conveyors, mobile belt conveyors, trough belt conveyors and high-angle belt conveyors (skirt side guard belt conveyors). The following is a comparative analysis of these forms in aggregate conveying:
|
Type |
Picture |
Conveying capacity range (t/h) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Applicable material particle size |
Application scenario |
Structural characteristics |
|
Fixed belt conveyor |
|
50~2000 |
0.8~2.5 |
≤150mm (commonly used) |
Main conveying section of aggregate production line, finished material conveying, silo filling, etc. |
Fixed installation position, stable operation, suitable for medium and long-distance continuous conveying |
|
Mobile belt conveyor |
|
30~800 |
0.5~1.6 |
≤100mm |
Temporary stacking, loading operation, flexible transportation |
With walking wheels, partially retractable, suitable for site Frequent changes |
|
Trough belt conveyor |
|
100~2500 |
1.0~2.5 |
≤200mm |
Mainly used for long-distance aggregate main conveying system |
Use multiple sets of trough rollers to support the belt to prevent material leakage |
|
Large-angle belt conveyor (skirt side guard belt conveyor) |
|
50~1000 |
0.6~1.5 |
≤80mm |
Limited space, large angle or vertical aggregate conveying |
Wavy side guard with cross partition structure, effectively prevent material from falling back, suitable for conveying at an angle greater than 30° |
Working principle of belt conveyor aggregate
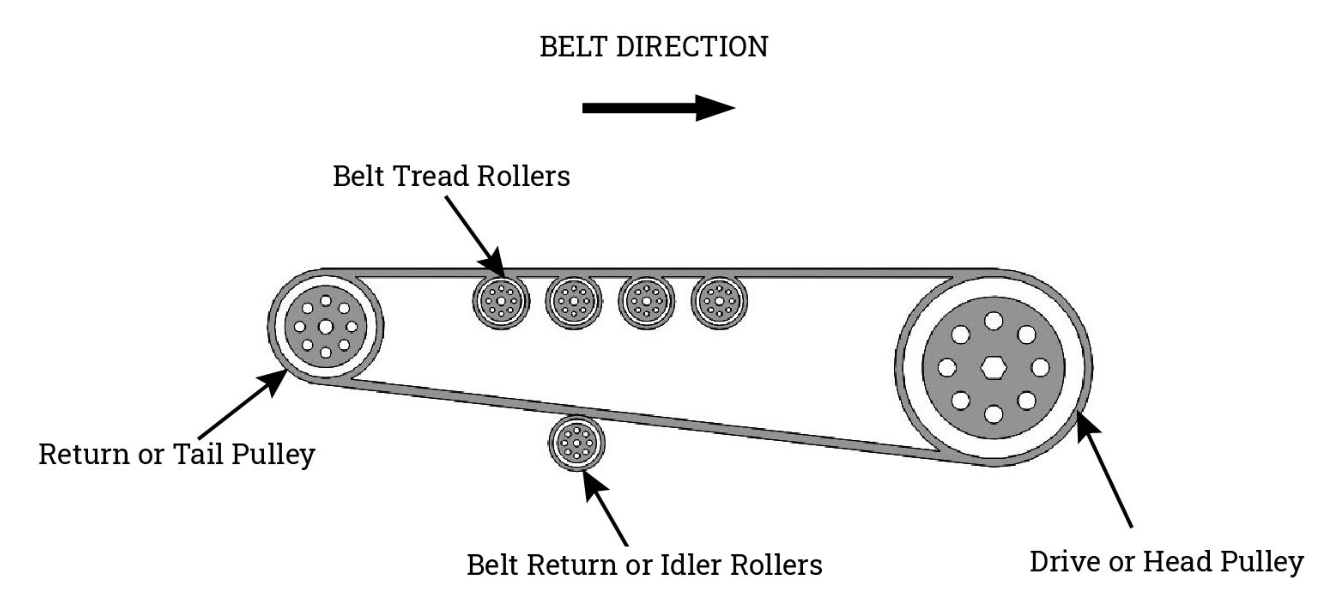
The belt conveyor aggregate is mainly composed of conveyor belt, drive device, roller, roller, frame and other components. The drive device drives the active roller to rotate, and the active roller drives the conveyor belt to move through friction, and the conveyor belt drives the driven roller to rotate, thereby realizing the continuous conveying of aggregate on the conveyor belt. During the conveying process, the roller is used to support the conveyor belt and aggregate, reduce the sagging and wear of the conveyor belt, and ensure the stability of the conveying.
Belt conveyors aggregate structure

Conveyor belt: wear-resistant rubber belt or steel cord belt, thickness ≥10mm
Roller: high-strength sealed roller, excellent dust and water resistance
Drive device: generally electric roller or motor with reducer combination
Tensioning device: common spiral tensioning and weight tensioning, long-distance conveyor is recommended to use weight tensioning
Cleaning device: tail scraper or empty section cleaner to prevent aggregate adhesion and belt deviation
Technical specifications of belt conveyor aggregate
|
Width (mm) |
Conveying length (m) Power (kw) |
Conveying length (m) Power (kw) |
Conveying length (m) Power (kw) |
Conveying speed (m/s) |
Conveying volume (t/h) |
|
400 |
≤10 3 |
12-15 3-4 |
15-30 4-7.5 |
1.25-2.0 |
30-60 |
|
500 |
≤10 3 |
12-15 4-5.5 |
15-30 5.5-7.5 |
1.25-2.0 |
40-80 |
|
650 |
≤10 4 |
12-15 7.5 |
15-30 7.5-11 |
1.25-2.0 |
80-120 |
|
800 |
≤10 4 |
12-15 7.5 |
15-30 7.5-15 |
1.25-2.0 |
120-200 |
|
1000 |
≤10 5.5 |
10-20 7.5-11 |
20-40 11-22 |
1.25-2.0 |
200-320 |
|
1200 |
≤10 7.5 |
10-20 7.5-15 |
20-40 15-30 |
1.25-2.0 |
290-480 |
|
1400 |
≤10 11 |
10-20 15-22 |
20-40 22-45 |
1.25-2.0 |
400-680 |
|
1600 |
≤10 15 |
10-20 22-30 |
20-50 30-75 |
1.25-2.0 |
600-1080 |
|
1800 |
≤10 18.5 |
10-20 30-45 |
20-50 45-110 |
1.0-2.0 |
800-1500 |
|
2000 |
≤10 22 |
10-20 45-55 |
20-50 55-132 |
1.0-2.0 |
1000-2000 |
|
2400 |
≤10 30 |
10-20 55-75 |
20-50 75-185 |
1.0-2.0 |
1500-3000 |
Common problems and solutions when conveying belt conveyor aggregate
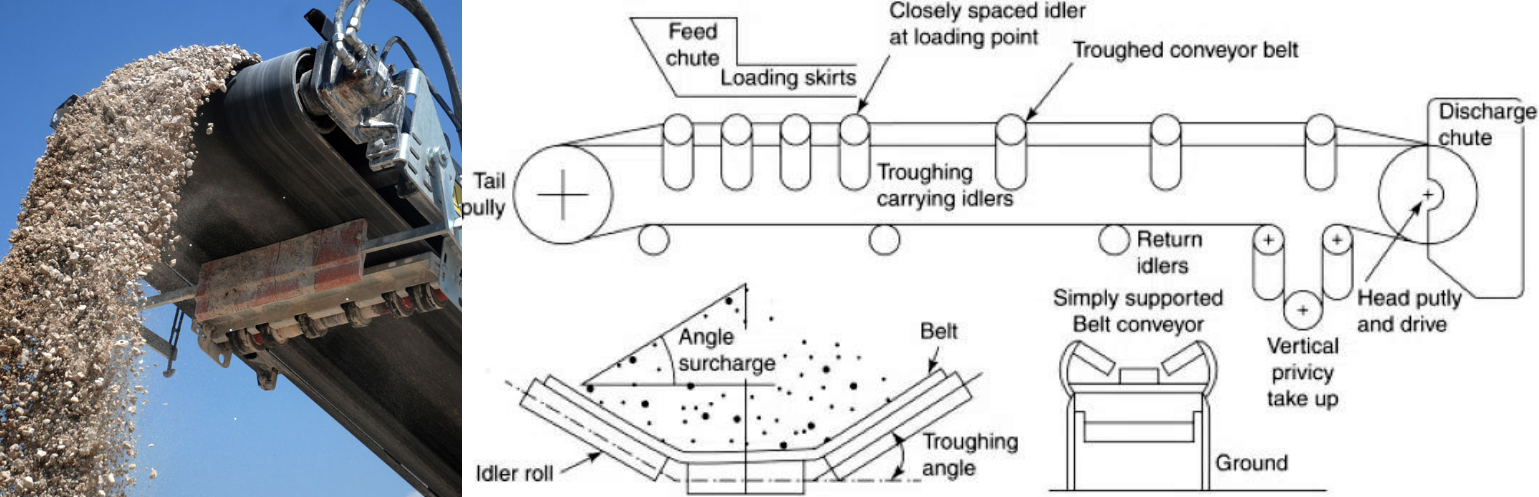
① Aggregate spillage: When the upward angle of the belt conveyor is too large, the friction between the aggregate and the belt is reduced, and the aggregate is easy to roll down along the belt; when there is a lot of aggregate accumulation per unit length, it is also easy to fall from both sides of the belt. The solution includes adjusting the degree of upward bending of the front and rear sides of the top of the conveyor belt through the diagonal support assembly to improve the blocking effect of aggregates; setting a suitable conveying speed and feeding amount to avoid excessive accumulation of aggregates; setting sidewalls or skirts on both sides of the belt to prevent aggregates from falling from the side.
② Belt deviation: The belt may deviate during operation, resulting in uneven conveying or even spilling of aggregates. The reasons may be improper belt installation, non-parallel roller axes, uneven material distribution, etc. It can be corrected by adjusting the position of the roller, installing a deviation adjustment device, and ensuring uniform material feeding.
③ Aggregate adhesion: For wet fine aggregates, such as river sand, some aggregates will adhere to the belt and be carried under the belt and fall, causing waste. A cleaning mechanism, such as a vibrating sheet, a cleaning roller, etc., can be set to shake off and clean the wet fine aggregates attached to the belt during the conveying process, so that it slides along the discharge guide groove.
④ Belt slippage: Long-term use or insufficient belt tension may cause the conveyor belt to age and slip, affecting the conveying efficiency. The belt tension can be adjusted through the tensioning mechanism, the aging belt can be replaced in time, the debris on the belt surface and the roller surface can be cleaned, and the friction can be increased.
Application of belt conveyor aggregate
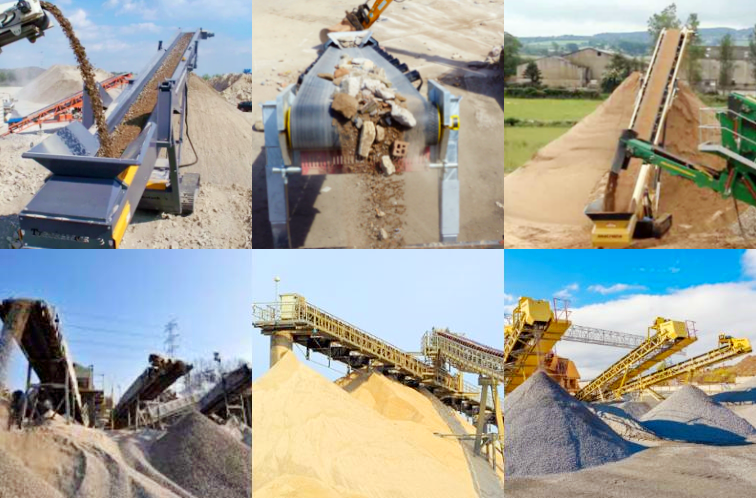

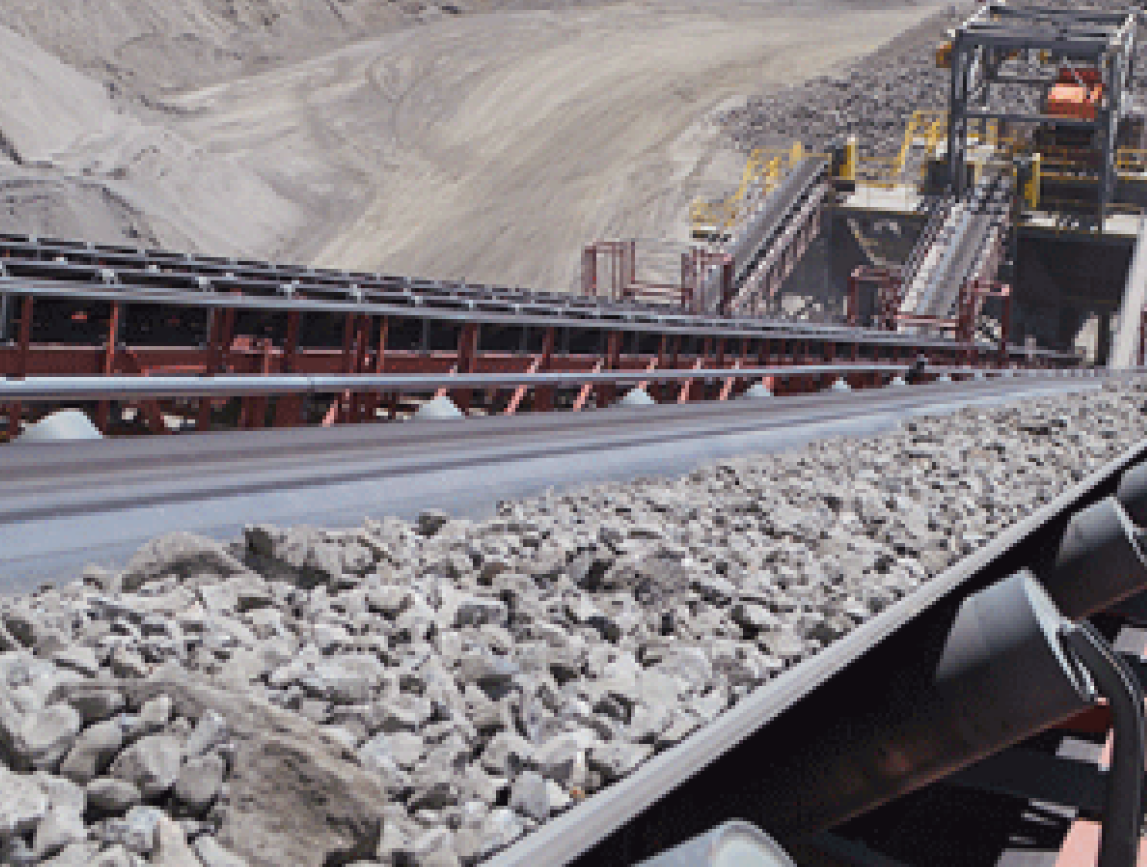
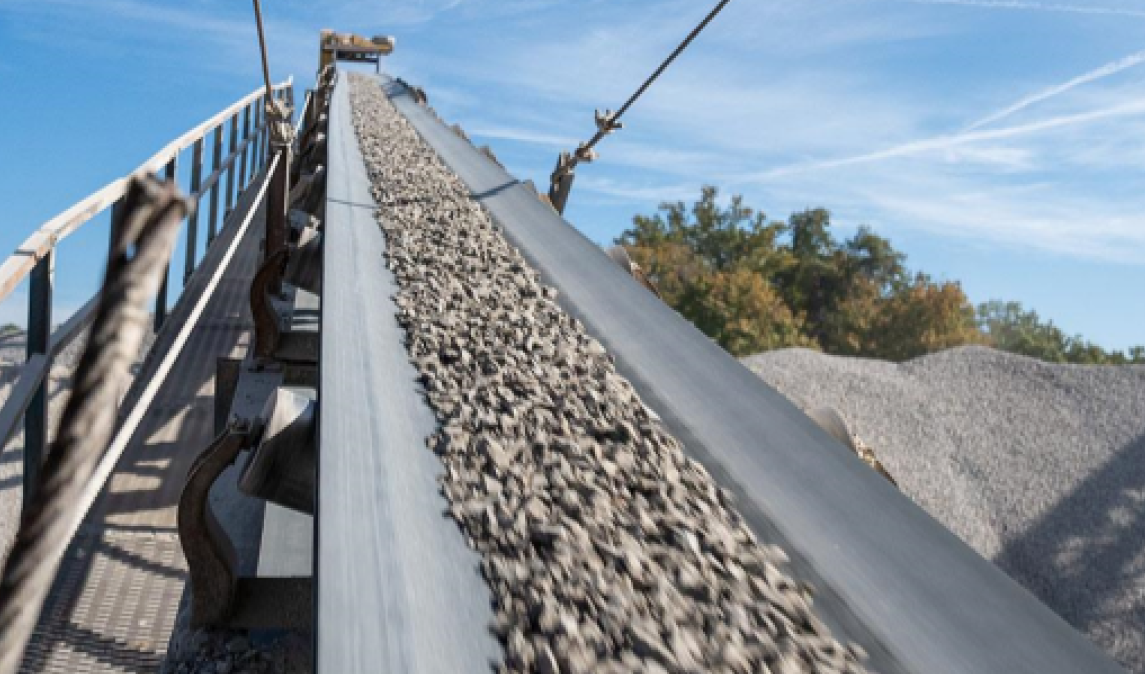
Belt conveyors aggregate play a significant role in aggregate applications: During mining, fixed belt conveyors transport the blasted gravel from the mining surface to the crushing workshop over a long distance and in large quantities; in concrete mixing stations, trough belt conveyors use U-shaped structures to stably transport aggregates such as sand and gravel to avoid spilling; mobile belt conveyors flexibly transport aggregates at construction sites and adapt to different unloading points; large-angle belt conveyors rely on skirt rib design to lift aggregates vertically to the top of the mixing building or storage bin in a narrow space. These four types of conveyors cover the entire process of aggregate mining, processing and use, effectively improving the efficiency and stability of aggregate transportation.
Typical application scenario examples
|
Application scenario |
Stone crushing production line |
Concrete mixing station |
Cement plant/mining system |
|
Image |
|
|
|
|
Transporting crushed aggregate from primary crusher to screening equipment or secondary crusher |
Used for feeding aggregate to batching machine |
Stacking system mobile belt conveyor is used to stack finished sand and gravel in the material yard |
Used for transporting aggregate from ore bin to the next processing link |
















