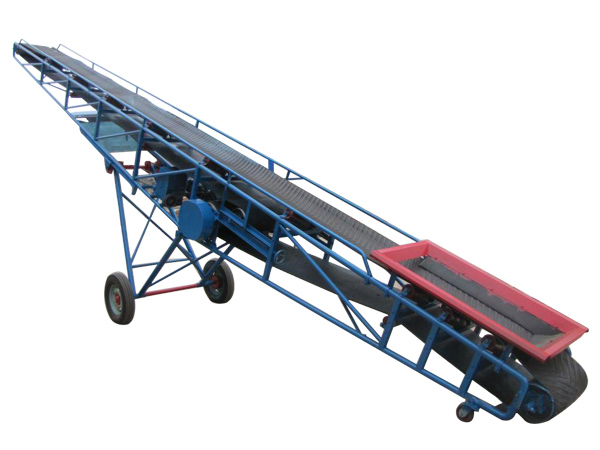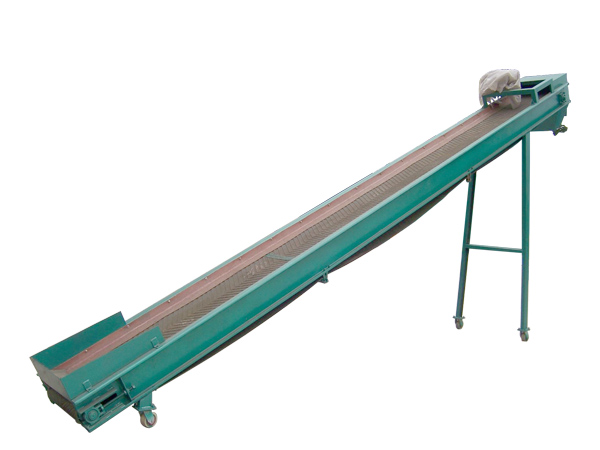
Belt Conveyor Feed
Belt conveyor feed is a commonly used equipment in agricultural breeding and feed processing industries. It is mainly used to automatically transport granular, powdered or block feed, improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Conveying capacity m³/h: 78-348
Belt width Bmm: 500-1400
Belt speed m/s: 0.8-4
What is a belt conveyor feed?
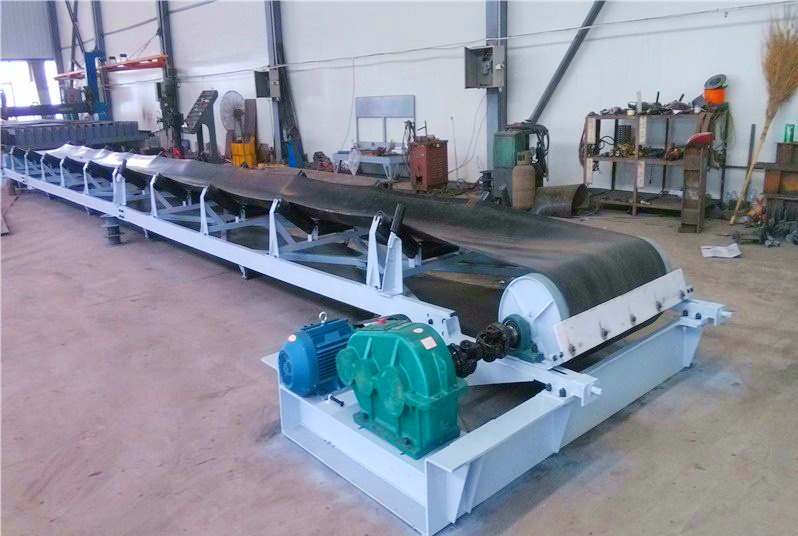

Belt conveyor feed is a conveying device that relies on a continuously running belt conveying medium (usually a rubber belt, PVC belt or canvas belt) to transport bulk or granular feed from one location to another. Its main function is to realize the automated and continuous conveying of feed, and it is widely used in farms, feed processing plants, grain storage and transportation systems and other occasions.
Types of belt conveyor feed
There are various types of feed conveyor belts available, each with different characteristics and advantages. Some of the most common types include:
①Belt conveyor feed

Features: Made of rubber or synthetic materials, with a flat surface, suitable for horizontal or small inclination angles.
Applicable scenarios: short-distance transportation of granular feed and powdered raw materials, suitable for various feeds, and can transport feed horizontally or obliquely.
Advantages: smooth operation, low noise, and low cost.
Disadvantages: not suitable for high humidity or sticky materials.
② Screw conveyor (auger)

Features: the material is pushed forward by the rotation of the spiral blade, suitable for closed environments.
Applicable scenarios: vertical or horizontal transportation of powdered or small-granular feed, suitable for conveying dry, free-flowing feed, and can transport feed horizontally or vertically.
Advantages: dustproof, suitable for narrow spaces.
Disadvantages: high energy consumption, easy to wear during long-distance transportation.
③ Bucket elevator
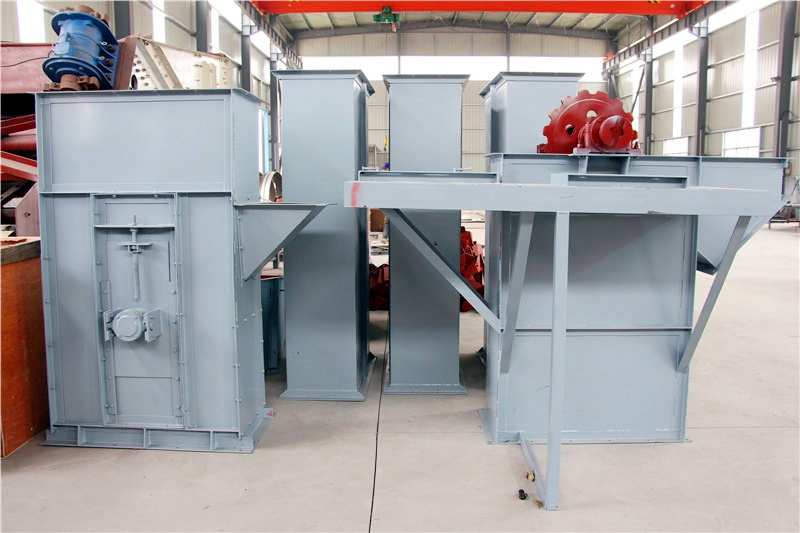

Features: Lift materials vertically through the hopper.
Applicable scenarios: Vertical transportation of raw materials from the bottom to the high-level equipment (such as the feeding port to the mixer).
Advantages: Small footprint and high transportation efficiency.
Disadvantages: High requirements for material fluidity.
Video of belt conveyor feed
What is the working principle of the belt conveyor feed?
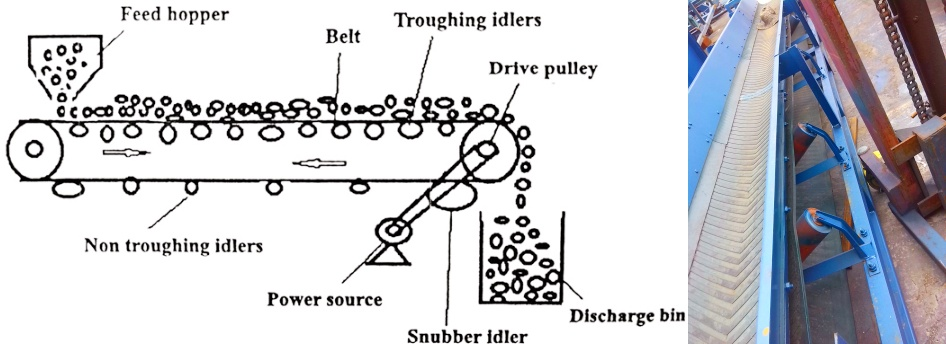
The belt conveyor feed is mainly composed of two end rollers and a closed conveyor belt tightly sleeved thereon. The roller that drives the conveyor belt to rotate is called the drive roller (transmission roller), and the other roller that only changes the direction of movement of the conveyor belt is called the redirection roller.
The drive roller is driven by an electric motor through a reducer, and the conveyor belt is dragged by the friction between the drive roller and the belt conveyor feed. The drive roller is generally installed at the discharge end to increase traction and facilitate dragging. The material is fed from the feeding end, falls on the rotating conveyor belt, and is driven by the friction of the conveyor belt to be transported to the discharge end for discharge.
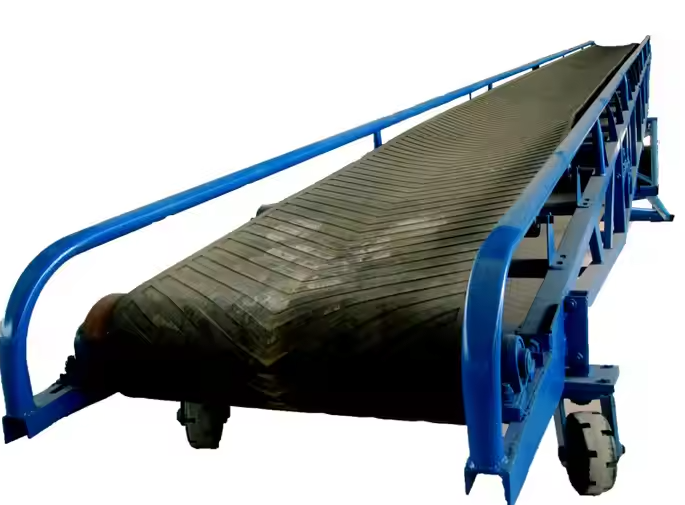
Structure of belt conveyor feed
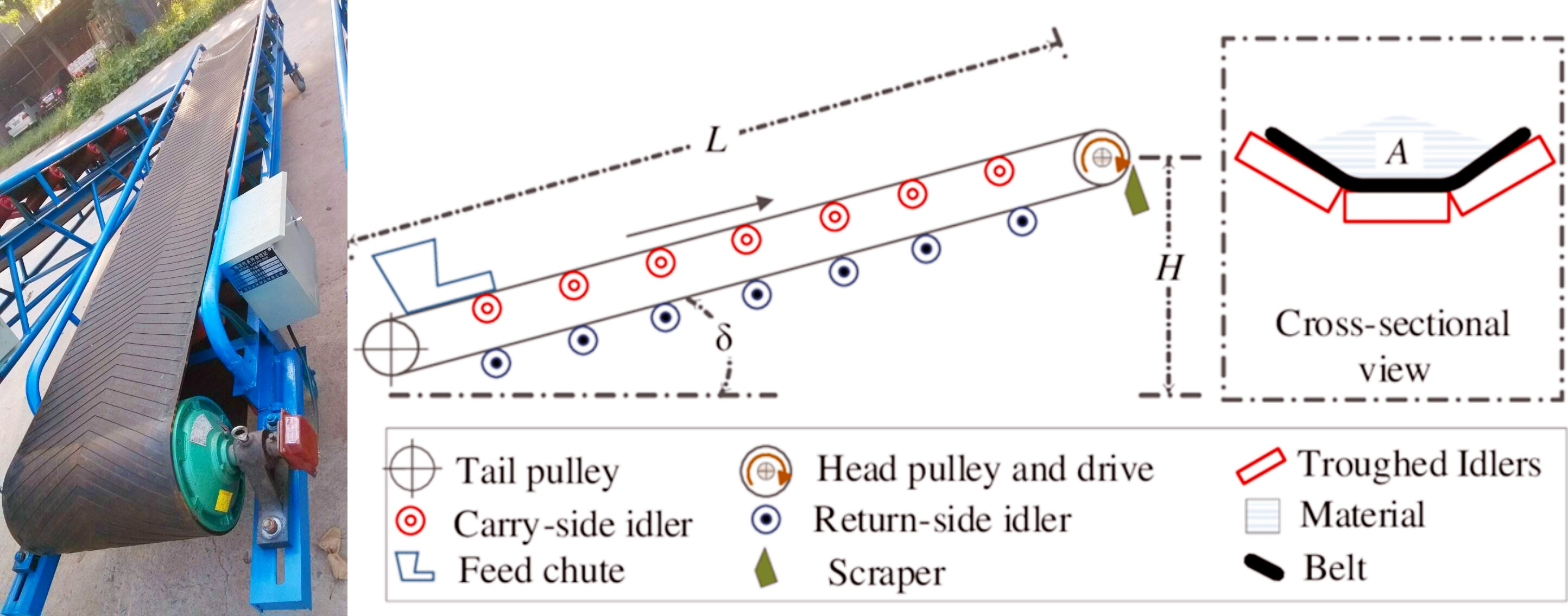
The structure of belt conveyor feed is designed to transport feed efficiently and stably, and usually consists of the following main parts:
Pipe belt: single-layer or multi-layer structure, enhanced tensile strength. The surface can be smooth or patterned (herringbone, corrugated) to increase the corrugation force and prevent the stack from slipping.
Drive device: The motor provides power, and the conveyor adjusts the motor to ensure smooth operation of pipeline transportation and adapt to different pipeline requirements.
Support frame: Supports the entire pipeline transportation system to ensure structural stability. Usually stainless steel, carbon steel or aluminum alloy, stainless steel and corrosive agents commonly used in the supply industry.
Rollers and support devices: Support the pipeline belt, reduce running resistance, and ensure smooth transportation.
Tensioning device: Adjust the tension of the pipeline belt to prevent relaxation or deviation. Screw tensioning, weight tensioning or hydraulic tensioning.
Guide and anti-deviation device: traction/stop rollers ensure that the belt conveyor feed runs on the correct track, and the anti-deviation switch can automatically detect and correct the deviation of the pipeline belt, which is common in long-distance pipeline systems.
What are the advantages of belt conveyors feed?
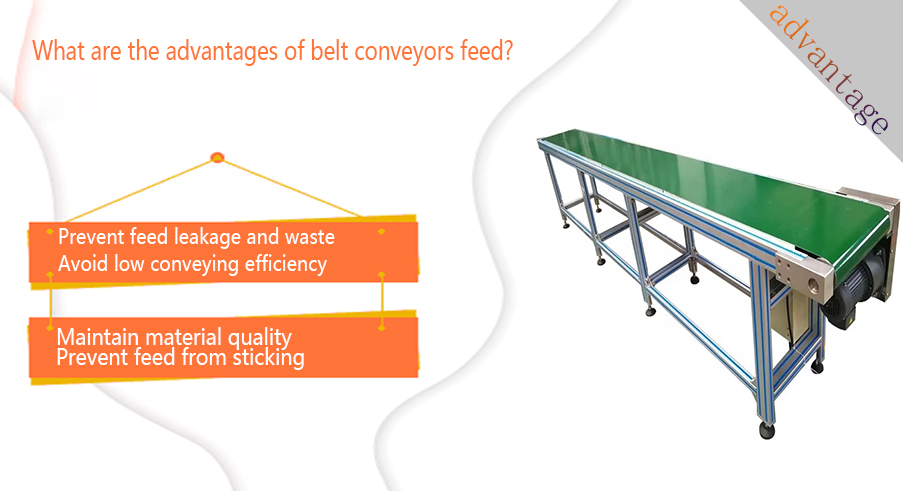
Prevent feed leakage and waste: Granular or powdered feed is easily spilled during transportation due to vibration, tilting or unsealed edges of the conveyor belt. By setting wavy or vertical sidewalls on both sides of the conveyor belt, the feed can be effectively prevented from slipping during tilted transportation or turning. Or flexible skirts can be added on both sides of the belt conveyor feed to form a certain groove with the belt body to improve the material holding capacity and reduce lateral leakage.
Avoid low conveying efficiency: Manual handling is inefficient and labor-intensive; traditional simple conveying methods may be slow and have a small conveying volume. Conveyor belts can achieve continuous and uninterrupted material transportation, greatly improving the conveying efficiency. Compared with intermittent manual handling, the efficiency is significantly improved.
Maintain material quality: In order to ensure the quality and safety of the feed, select standard conveyor belt materials, such as food-grade rubber, PVC or PU, to ensure that the quality of the feed is not affected during transportation. Reasonably adjust the tension and running speed of the belt conveyor feed to avoid excessive friction and extrusion of the feed during transportation, and prevent the feed particles from breaking or deteriorating.
Prevent feed from sticking: For feed that is easy to stick, such as feed containing oil or high moisture, a conveyor belt material with a smooth surface and not easy to adhere to the material can be selected, which can effectively reduce the adhesion of the material on the belt conveyor feed. During the feed processing and transportation process, strictly control the humidity and temperature of the material to reduce the possibility of the material sticking due to moisture or heat.
Technical parameters of belt conveyor feed

|
Bearing roller form |
Belt speed (m/s) |
Belt width B (mm) |
650 |
800 |
1000 |
1200 |
1400 |
|
500 |
650 |
800 |
1000 |
1200 |
1400 |
||
|
Conveying volume Q (t/s) |
650 |
800 |
1000 |
1200 |
1400 |
||
|
Grooved drag roller |
0.8 |
78 |
131 |
||||
|
Trough roller |
1.0 |
97 |
164 |
278 |
435 |
655 |
891 |
|
1.25 |
122 |
206 |
348 |
544 |
819 |
1115 |
|
|
1.6 |
156 |
264 |
445 |
696 |
1048 |
1427 |
|
|
2.0 |
191 |
323 |
546 |
853 |
1284 |
1748 |
|
|
2.5 |
232 |
391 |
661 |
1033 |
1556 |
2118 |
|
|
3.15 |
- |
- |
824 |
1233 |
1858 |
2528 |
|
|
4.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2202 |
2996 |
|
|
Parallel roller |
0.8 |
41 |
67 |
118 |
- |
- |
- |
|
1.0 |
52 |
88 |
147 |
230 |
345 |
460 |
|
|
1.25 |
66 |
110 |
184 |
288 |
432 |
588 |
|
|
1 .6 |
84 |
142 |
236 |
368 |
553 |
753 |
|
|
Parallel drag roller |
2.0 |
103 |
174 |
289 |
451 |
677 |
922 |
|
2.5 |
125 |
211 |
350 |
546 |
821 |
111 |
|
Application of belt conveyor feed
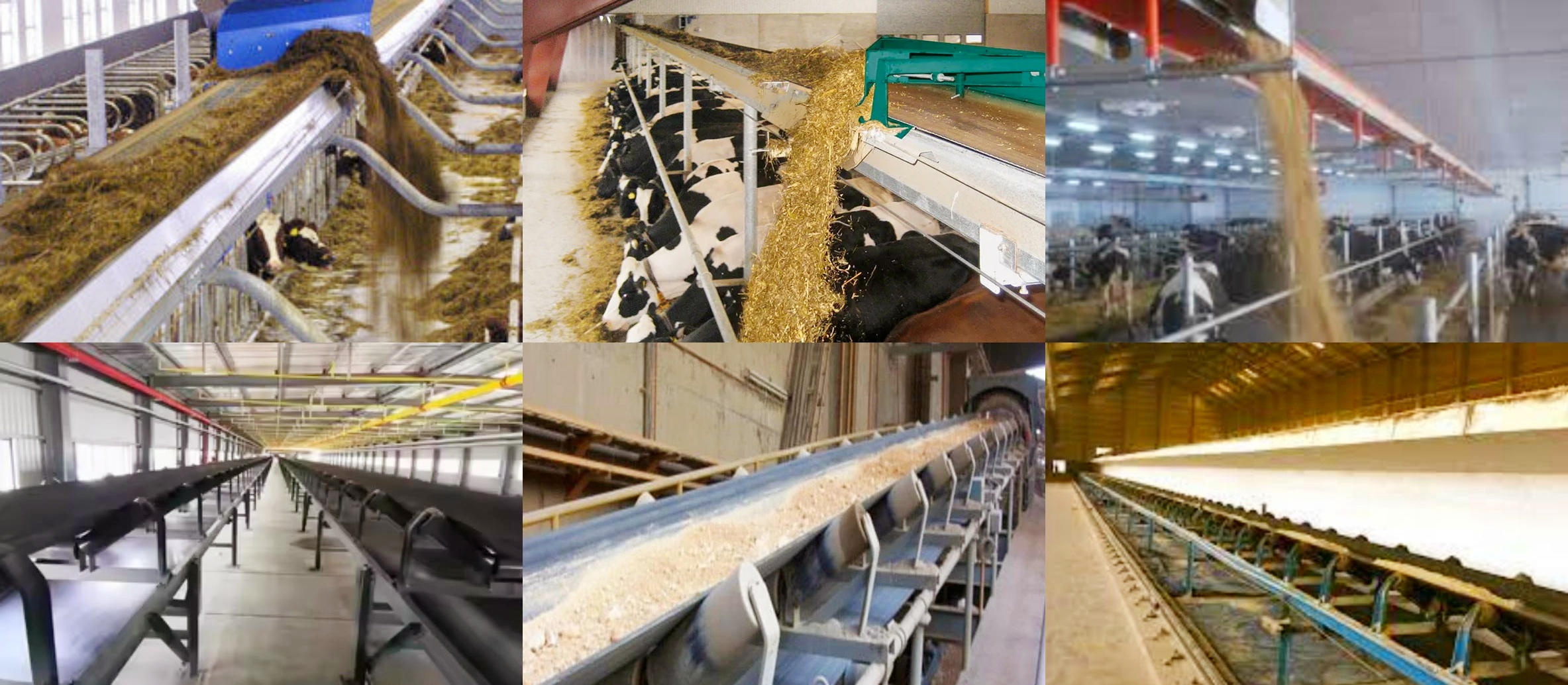

Belt conveyor feed is widely used in feed-related fields. It runs through all aspects of feed production, processing, storage, transportation and breeding, greatly improving the efficiency and quality of feed processing. In the feed production process, belt conveyor feed is an important part of the automated production line. It is responsible for transporting raw materials from the warehouse to the production workshop, and after crushing, mixing, granulation and other processes, it transports the finished feed to the packaging or storage area. It transports feed from silos or hoppers to feeding equipment, distributes feed to livestock pens or paddocks, and transports feed from one processing point to another.
Feed factory raw material conveyor line
Automatic feeding system for livestock and poultry farms
Loading and unloading feed in granaries
Transferring feed materials at ports or stations
Key points for selecting belt conveyor feed
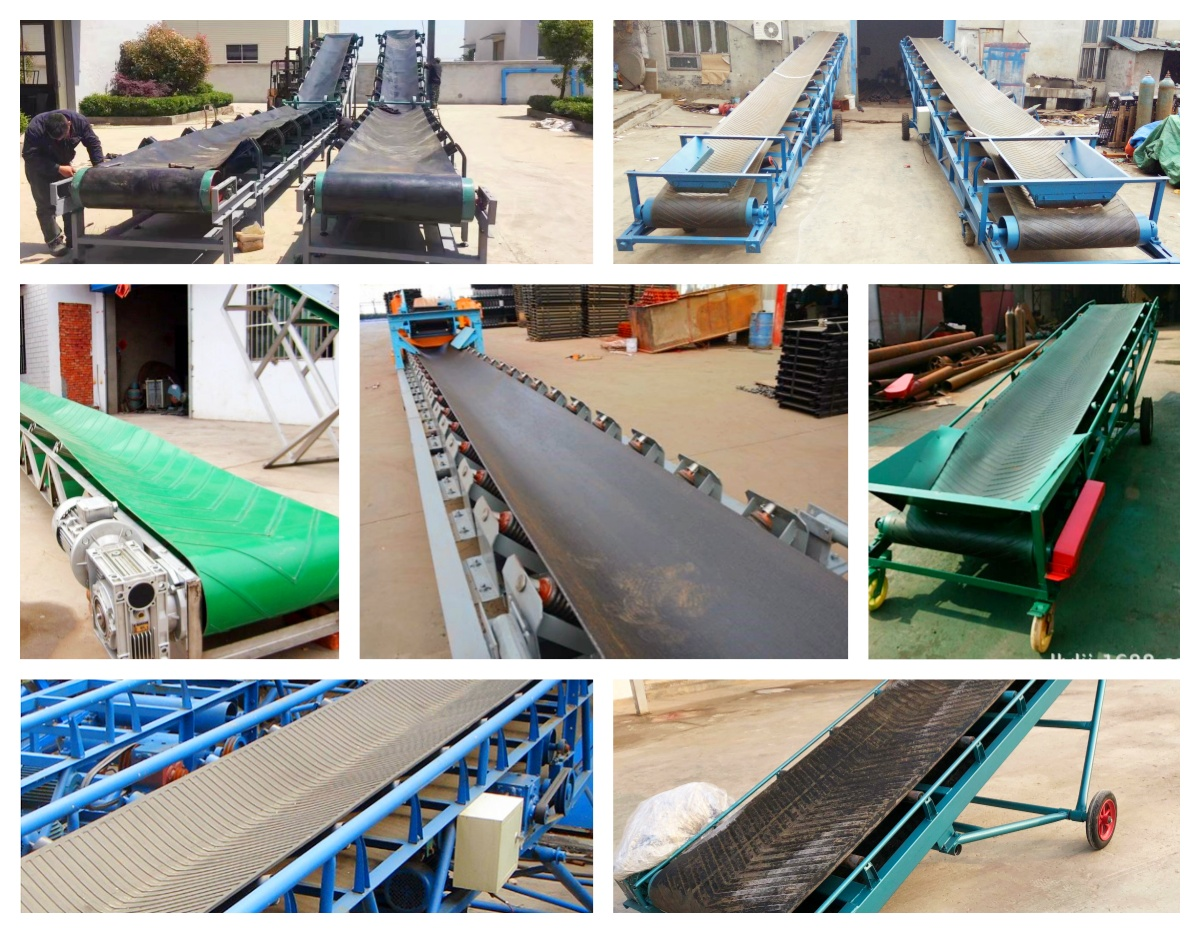

Conveying material characteristics: Select the appropriate conveyor belt type and specifications according to the form (powder, granular, block, bagged, etc.), particle size, humidity, density and other characteristics of the feed. For example, for powdered feed, it is advisable to use a trough-type or sidewall belt conveyor feed to prevent spillage; for block feed with higher density, it is necessary to choose a chain plate or heavy-duty rubber conveyor belt with strong load-bearing capacity.
Conveying capacity requirements: According to the actual output and conveying requirements in the feed processing or breeding process, determine the conveying capacity of the conveyor belt, that is, the amount of material that needs to be conveyed per unit time.
Conveying distance and height: Consider the horizontal distance and lifting height that the feed needs to be conveyed, and select the appropriate conveyor belt length and conveying angle. For long-distance transportation, a conveyor belt with high strength and good wear resistance can be selected; for occasions with large lifting heights, a large-angle corrugated sidewall belt conveyor feed is a better choice.
Working environment conditions: If the working environment is humid, corrosive gas or dusty, you should choose a conveyor belt material with moisture-proof, corrosion-resistant and dust-proof properties. If the ambient temperature is high or low, you need to choose a conveyor belt that can adapt to the corresponding temperature range.








