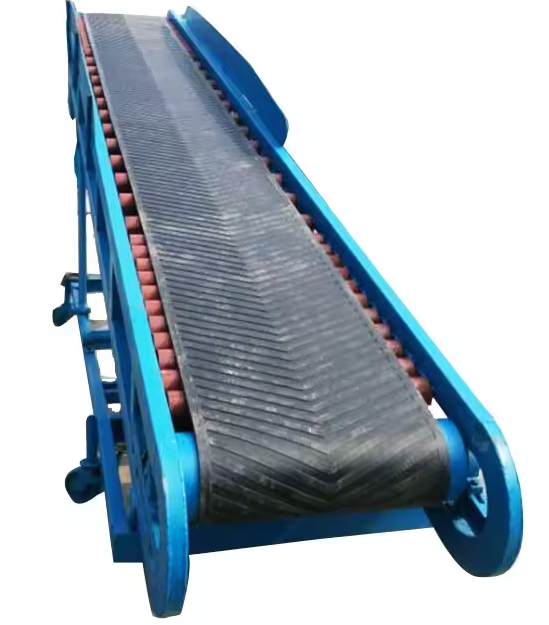
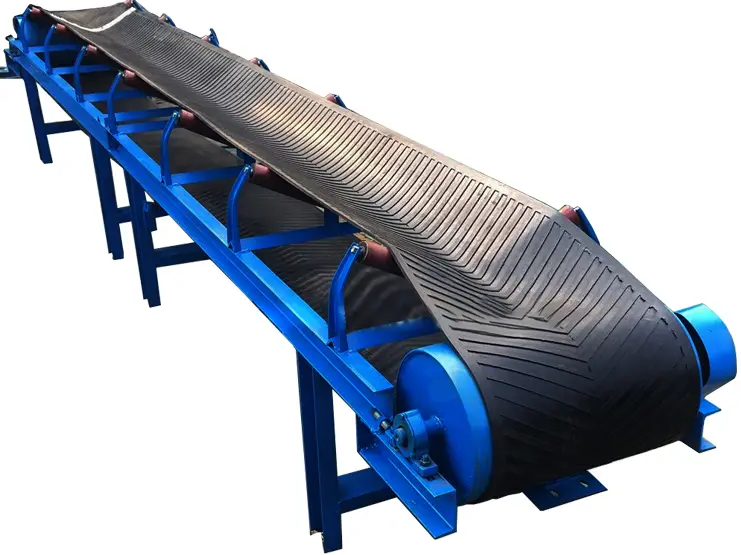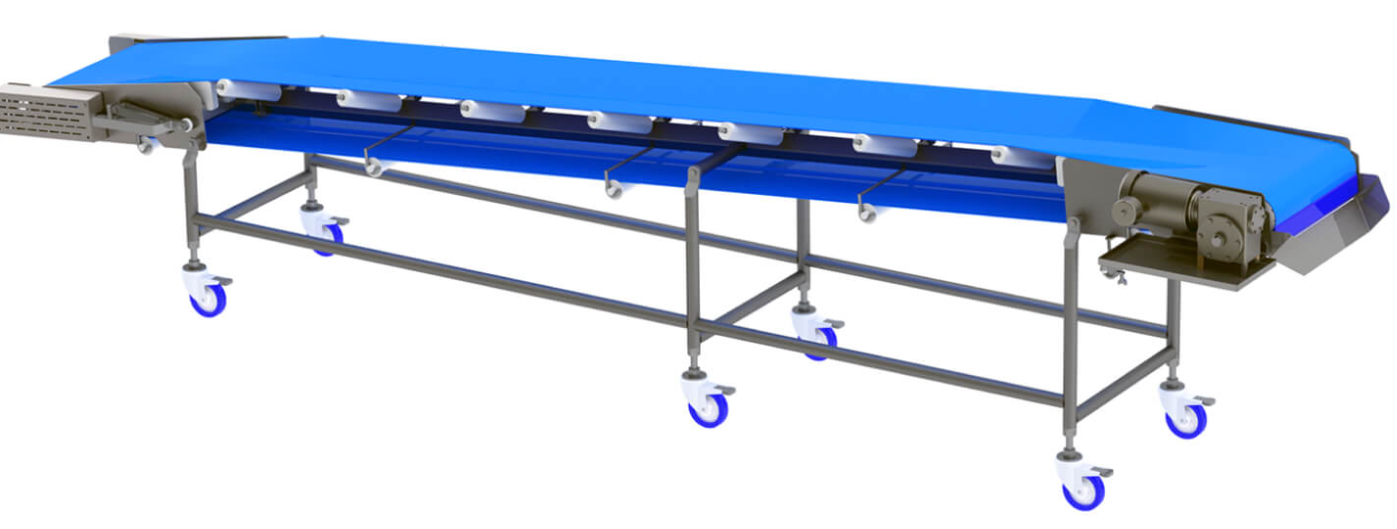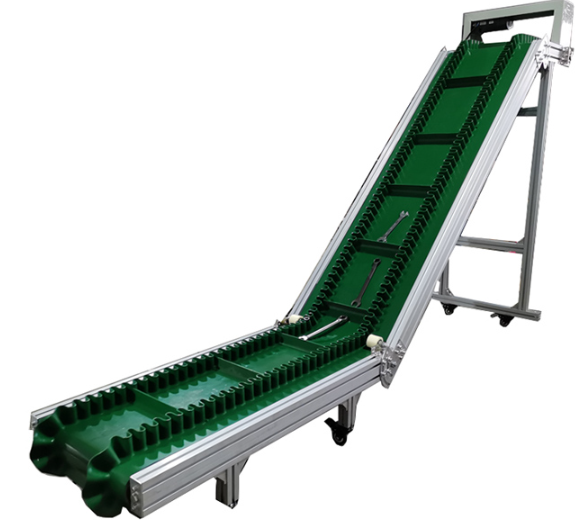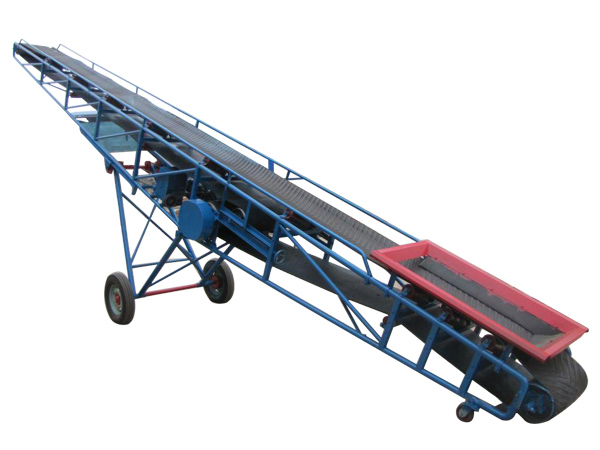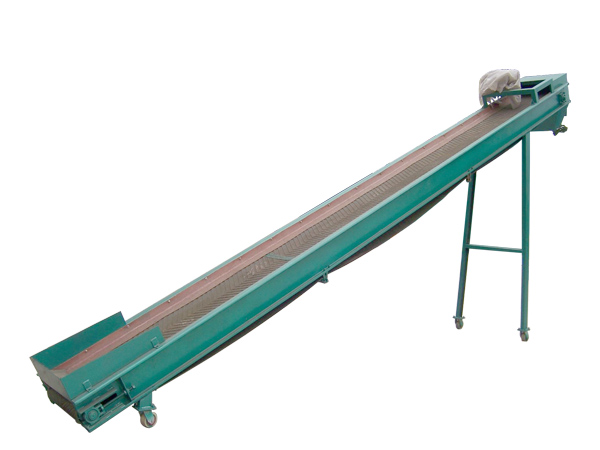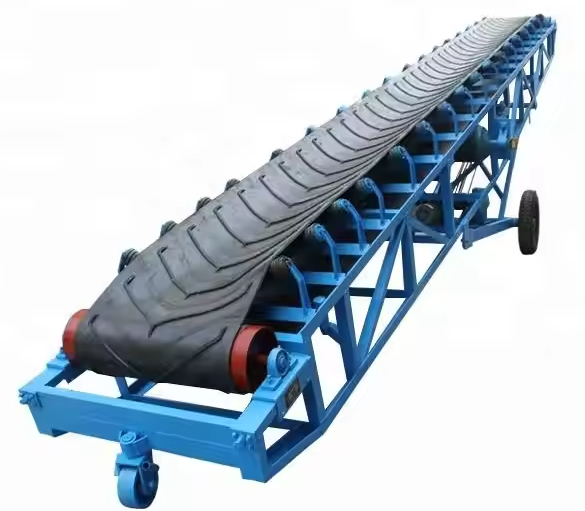
Belt Conveyor Ore
Belt conveyor ore is a continuous transportation equipment widely used in industrial fields such as mines, quarries, ports, etc. It is mainly used for horizontal or inclined transportation of bulk materials such as ore, coal, sand and gravel.
Conveying capacity: 50-500 tons/hour
Belt speed: 1.0-4.0 m/s
Belt width: 500-1600 mm
Product description
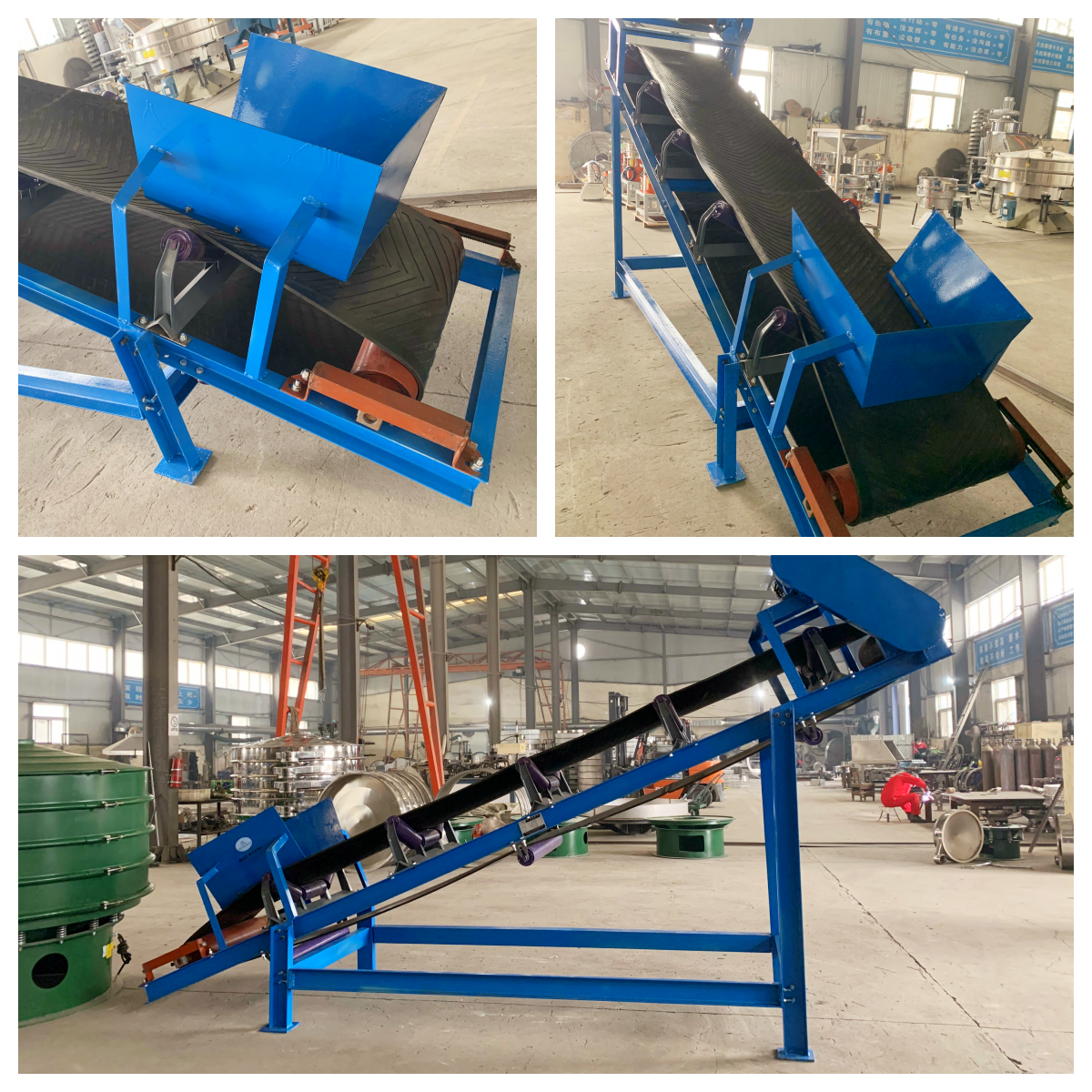

Belt conveyor ore is a mechanical equipment used for continuous transportation of bulk ore materials. It is mainly composed of drive device, conveyor belt, roller, roller, tensioning device and frame. Its working principle is to drive the conveyor belt to run through the drive device to transport the ore loaded on the conveyor belt from one place to another.

During the ore transportation process, it is sometimes necessary to screen the ore to meet the requirements of the subsequent process for the particle size of the material. The screening mesh is an indicator to measure the size of the screen aperture, which refers to the number of mesh holes per inch length. The common ore screening mesh range is wide. This equipment is suitable for block or powdered ores with a particle size between 0 and 300 mm. Some materials that need to be screened can be used in combination with vibrating screening equipment, and are often pre-processed with screens with a screening mesh between 10 and 80 meshes. The conveyor belt width is commonly 500mm, 650mm, 800mm and other specifications. For example, the coarsely crushed ore may need to pass through a 5-20 mesh screen to remove oversized materials, while the ore pulp after grinding may need to pass through a 100-300 mesh or even finer screen for classification.
What types of belt conveyors ore are there?
|
Type |
Fixed belt conveyor |
Mobile belt conveyor |
Trough belt conveyor |
Tubular belt conveyor |
|
Image |
|
|
|
|
|
Features |
Simple structure, stable operation, easy maintenance |
Can move with the working surface, suitable for temporary working points |
The upper roller is trough-shaped to prevent the side leakage of bulk materials |
The belt body is tubular and has good sealing |
|
Capacity |
28-800 cubic meters/hour |
28-800 cubic meters/hour |
28-800 cubic meters/hour |
160 cubic meters/hour |
|
Length |
20 meters |
6 meters |
1.7-20 meters |
1.7-6 meters |
|
Applicable scenarios |
Main transportation system of mines, long-distance and large-capacity transportation |
Temporary stacking, short-distance transportation |
Bulk ore, sand and gravel |
Need to cross complex terrain |
|
Type |
Large-angle sidewall belt conveyor |
Climbing belt conveyor |
Telescopic belt conveyor |
Multi-stage combined belt conveyor system |
|
Pictures |
|
|
|
|
|
Features |
With skirts and diaphragms, it can convey at large angles or vertically |
Adapt to certain slopes (generally ≤20°), some with anti-slip patterned belts |
Adopt telescopic mechanism design to extend or shorten the length of the conveyor belt |
Composed of multiple belt conveyors, it can adapt to complex lines |
|
Capacity |
28-800 cubic meters/hour |
50-400 tons/hour |
50-400 tons/hour |
28-1000 cubic meters/hour |
|
Length |
20 meters |
2.7-12 meters |
3-26 meters |
1.7+ meters |
|
Applicable scenarios |
Loading, silo filling, limited space |
Surface transportation to material piles, height difference |
Applicable to long distances |
Large-scale mining transportation system |
Working principle of belt conveyor ore
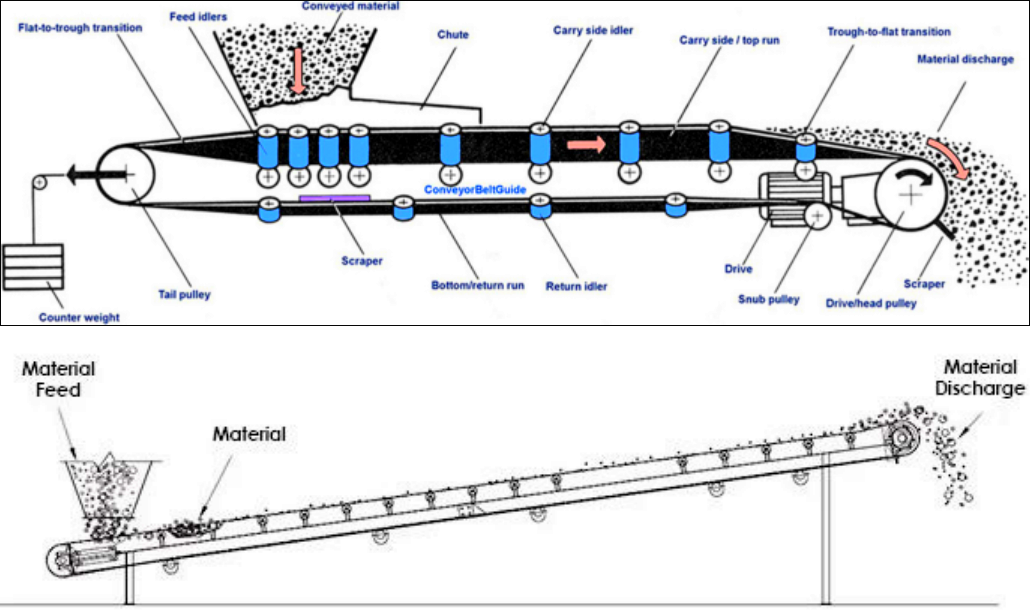
① Friction transmission principle: The belt conveyor ore is mainly composed of two end rollers and a closed conveyor belt tightly sleeved thereon. The roller that drives the conveyor belt to rotate is called the drive roller, and the other roller that only changes the direction of movement of the conveyor belt is called the redirecting roller. The driving roller is driven by the motor through the reducer, and the conveyor belt is dragged by the friction between the driving roller and the conveyor belt to realize the transportation of ore.
② The synergistic effect of gravity and friction: When the conveyor belt is running, the ore will be tightly attached to the conveyor belt due to gravity. At the same time, the friction between the conveyor belt and the ore enables the ore to move with the conveyor belt, thereby forming a material conveyor line from the initial feeding point to the final unloading point on a certain conveyor line.
Basic structural composition of belt conveyor ore
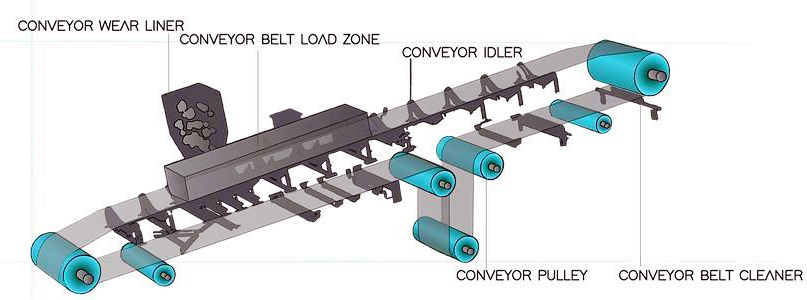
Belt conveyor ore is a device used to transport ore and other materials from one place to another. It usually consists of the following parts:
Conveyor belt: The main part of the ore conveyor, usually using wear-resistant rubber belt or steel wire core conveyor belt.
Drive device: includes motor, reducer and driving roller, used to provide power.
Roller system: supports the conveyor belt and materials, divided into upper roller, lower roller, buffer roller, etc.
Tensioning device: maintains the appropriate tension of the conveyor belt, common types are spiral tensioning and heavy hammer tensioning.
Head and tail frame: including head roller and tail roller, which are the starting and ending ends of the conveyor belt.
What are the advantages of belt conveyor ore?
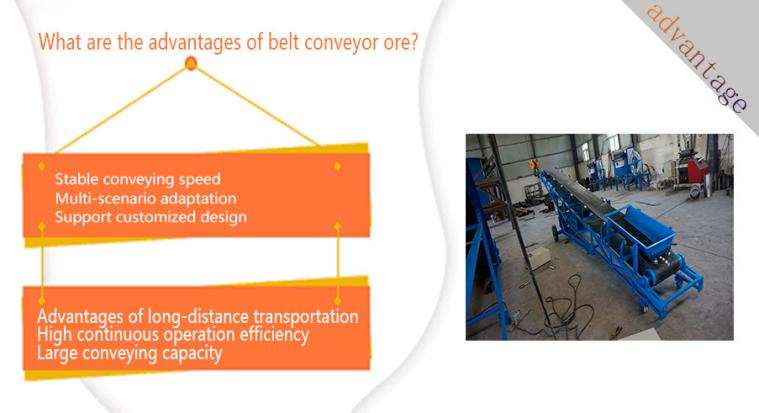
Stable conveying speed: with the automatic control system, the conveying volume can be accurately controlled to meet the continuous feeding needs of the production line.
Adapt to complex terrain: can adapt to the high and low terrain of the mine through bending and tilting design (such as large-angle belt conveyor), reduce the restrictions of terrain on transportation routes, and shorten the transportation distance.
Multi-scenario adaptation: can be seamlessly connected with mining equipment (such as crushers, screening machines) and storage systems (such as ore bins and material piles) to form an automated transportation network.
Support customized design: select belts of different materials and specifications (such as acid and alkali resistant belts, anti-slip belts) according to the characteristics of the ore (humidity, particle size, density).
Advantages of long-distance transportation: the conveying distance of a single machine can reach several kilometers (such as tubular belt conveyors), and multiple machines in series can achieve ultra-long-distance transportation of tens of kilometers, without the need for reprinting in the middle, reducing material loss and equipment investment.
High continuous operation efficiency: It can realize continuous transportation of ore, avoid the start-stop loss of intermittent transportation (such as truck transportation), and transport more per unit time, which is especially suitable for high-intensity operations in large-scale mines.
Large conveying capacity: Belt conveyors can realize large-capacity, long-distance, and high-speed continuous transportation, and can transport a large amount of ore per unit time, which is especially suitable for scenarios where large-scale transportation is required in mining operations. Common bandwidths are 500mm to 2400mm.
Common technical parameters and models of belt conveyors ore
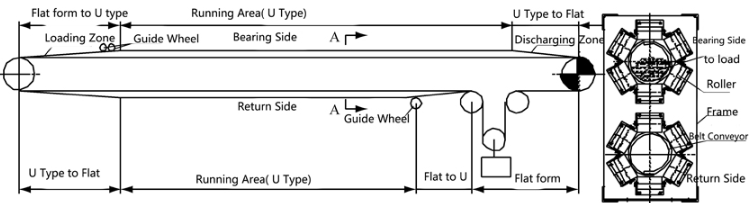
The models of belt conveyors ore are mostly distinguished by parameters such as bandwidth (B), belt speed (V), and conveying capacity (Q). The following are examples of common specifications:
|
Model |
bandwidth (mm) |
conveying speed (m/s) |
conveying capacity (t/h, calculated based on bulk density 1.6) |
|
B500 |
500 |
0.8~2.5 |
78~230 |
|
B650 |
650 |
1.0~2.5 |
131~386 |
|
B800 |
800 |
1.0~2.5 |
278~600 |
|
B1000 |
1000 |
1.0~3.15 |
435~1000 |
|
B1200 |
1200 |
1.25~3.15 |
655~1400 |
Note: The above data are reference values under conventional horizontal conveying conditions. The actual conveying capacity is affected by factors such as inclination, material properties, and conveying length.
Application of Belt Conveyor Ore

Belt conveyor ore is a kind of continuous conveying equipment widely used in mining, metallurgy, electricity, coal, building materials and other industries. It is mainly used for medium and long distance and large-scale transportation of bulk materials such as ore, coal, sand and gravel. It has a simple structure, stable operation and high conveying efficiency. It is one of the core equipment in the current ore transportation system.
Open-pit mine: Ore needs to be transported from the mining site to the crushing station or screening station. Traditional automobile transportation methods are costly and polluting, while belt conveyors can achieve continuous, efficient and automated transportation, reducing energy consumption and labor costs.
Underground mine: Belt conveyors ore are used to transport ore from the mining face to the main transportation tunnel, and then transport it to the ground through the main conveyor line. Compared with mine car transportation, this method reduces the number of transfers and improves transportation efficiency.
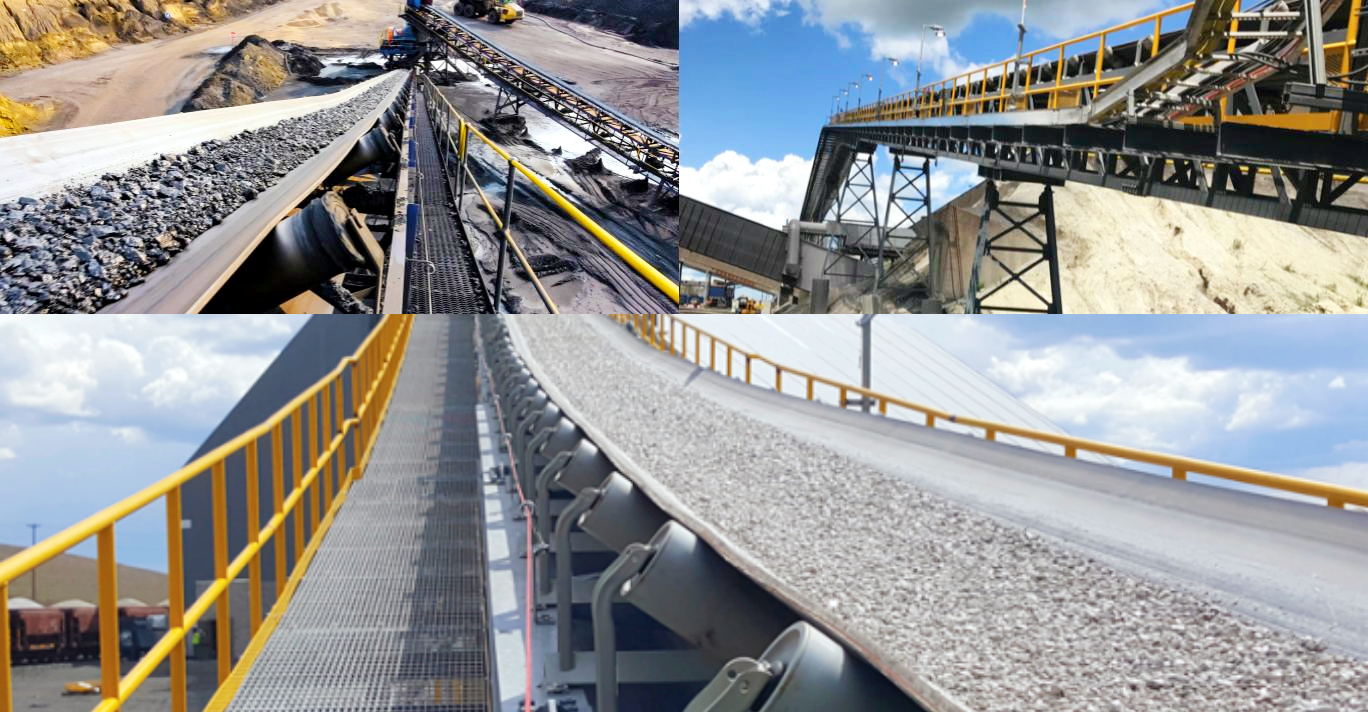

Ore crushing and screening system: Belt conveyors ore are often used to connect crushers, screeners, ore storage bins and other equipment to achieve orderly transportation of materials. In the whole process, the belt conveyor is responsible for conveying the coarsely crushed, medium-crushed or screened ore to the next process according to the process route.
Ore yard and loading station: In the finished product yard or loading system, the belt conveyor is used for ore stacking, loading and shipping operations, and is often used in conjunction with a stacker-reclaimer, bucket wheel excavator or loading system.
Common problems and solutions for belt conveyors ore
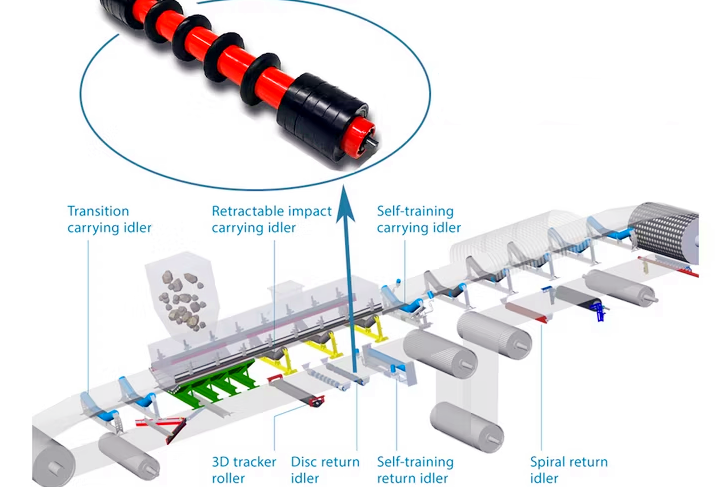
|
Common problems |
Possible causes |
Solutions |
|
Belt deviation |
Uneven belt tension, improper installation of rollers/idlers, eccentric loading of materials |
Adjust the tensioning device, correct the position of rollers and idlers, and control the centering of materials |
|
Belt slippage |
Insufficient tension, low friction coefficient of roller surface, excessive load |
Adjust the tensioning device, increase the rubber coating of rollers, and reduce the load |
|
Belt breakage |
Overload operation, belt aging or quality problems, sharp and hard objects in the material |
Control the conveying volume, regularly replace the aging belt, and use impact-resistant conveyor belts |
|
Roller damage/stuck |
Poor roller quality, poor lubrication, foreign matter entering the roller |
Replace high-quality rollers, regular maintenance, and install sealing devices to prevent foreign matter from intruding |
|
Roller slippage or non-rotation |
Bearing damage, material accumulation stuck, insufficient drive power Sufficient |
Check the bearings and replace them, clean up the accumulated materials, and replace the motor with the appropriate power |
|
Conveyor belt is seriously worn |
Material impact is large, the conveyor belt and the structural parts are rubbed, and the rollers rotate poorly |
Install the buffer device, adjust the structural position, and replace the worn parts in time |
|
Motor overheats or burns |
Excessive load, poor ventilation, long-term overload operation of the motor |
Reasonable control of the conveying volume, check the motor cooling system, and use overload protection devices |
|
Material spillage |
Uneven conveyor belt joints, too fast belt speed, unreasonable design of the guide trough |
Adjust the joint process, control the belt speed, and optimize the guide trough structure |
|
Conveyor belt accumulation |
Sweeper is damaged or failed, the material is wet and sticky |
Replace or adjust the sweeper, and select a sweeping device suitable for wet materials |
Selection suggestions for belt conveyors ore

Material: Ore (such as iron ore, copper ore, etc.), usually with large particle size and high density.
Particle size: If the particle size is greater than 100mm, it is recommended to choose a conveyor belt ore with strong impact resistance (such as steel wire rope core or steel wire mesh core belt).
Humidity and viscosity: Wet ore is easy to adhere, so an effective sweeper or scraper device is required. It is recommended to choose a moisture-resistant and non-slip roller in high-humidity working conditions.
Temperature: For high-temperature pre-smelting transportation, a heat-resistant conveyor belt (such as a rubber belt that can withstand 150℃ or 200℃) is required.
Abrasion resistance: It is recommended to use a highly wear-resistant rubber surface conveyor belt, or add buffer rollers and linings in the receiving section.
















